
Back بيتانين Arabic بتانین AZB Betanin BS Betanin Czech Betanin German Betanina Spanish Betanina Basque بتانین Persian Betaniini Finnish Bétanine French
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
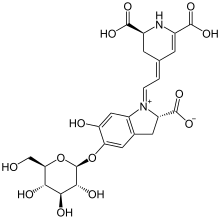
(2S)-1-{2-[(2S)-2,6-dicarboxy-2,3-dihydropyridin-4(1H)-ylidene]ethylidene}-5-(β-d-glucopyranosyloxy)-6-hydroxy-2,3-dihydro-1H-indol-1-ium-2-carboxylate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.753 |
| E number | E162 (colours) |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C24H26N2O13 | |
| Molar mass | 550.47 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Betanin, or beetroot red, is a red glycosidic food dye obtained from beets; its aglycone, obtained by hydrolyzing the glucose molecule, is betanidin. As a food additive, its E number is E162.[1] As a food additive, betanin has no safety concerns.[1]
The color of betanin depends on pH; between pH four and five, it is bright bluish-red, becoming blue-violet as the pH increases. Once the pH reaches alkaline levels, betanin degrades by hydrolysis, resulting in a yellow-brown color.[citation needed]
Betanin is a betalain pigment, together with isobetanin and other betacyanins.[2]
- ^ a b EFSA Panel on Food Additives and Nutrient Sources added to Food (9 December 2015). "Scientific Opinion on the re-evaluation of beetroot red (E 162) as a food additive". EFSA Journal. 13 (12): 4318. doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2015.4318.
- ^ Polturak G, Aharoni A (January 2018). ""La Vie en Rose": Biosynthesis, Sources, and Applications of Betalain Pigments". Molecular Plant. 11 (1): 7–22. doi:10.1016/j.molp.2017.10.008. PMID 29081360.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search