
Back الإمبراطورية البيزنطية تحت حكم السلالة الليونية Arabic Βυζαντινή Αυτοκρατορία υπό τη Δυναστεία του Λέοντα Greek Imperio bizantino bajo la dinastía de León Spanish امپراتوری بیزانس تحت خاندان لئونی Persian Impero bizantino durante la dinastia trace Italian ბიზანტიის იმპერია ლეონიდების მმართველობისას Georgian 레오 왕조 치하의 동로마 제국 Korean Império Bizantino sob a dinastia leonina Portuguese Leo Hanedanı döneminde Bizans İmparatorluğu Turkish لیونی شاہی سلسلہ کے تحت بازنطینی سلطنت Urdu
Byzantine Empire
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 457–518 | |||||||||
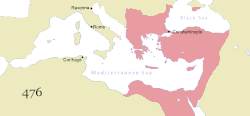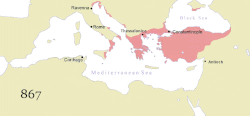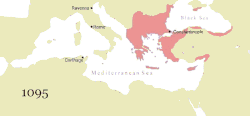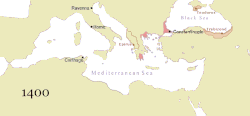
 The territory of the Eastern Roman Empire under the Leonid dynasty in 480. The Western Roman Empire, depicted in light purple, collapsed in 476/480, though the regions depicted nominally continued to be under Roman rule as vassals of the Eastern Empire. Orange is the Western Roman rump state at the time of Syagrius, now called the Kingdom of Soissons | |||||||||
| Capital | Constantinople | ||||||||
| Common languages | Latin, Greek | ||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||
| Emperor | |||||||||
• 457–474 | Leo I | ||||||||
• 474–474 | Leo II | ||||||||
• 474–491 | Zeno | ||||||||
• 475–476 | Basiliscus | ||||||||
• 491–518 | Anastasius I | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
• accession of Leo I the Thracian | 7 February 457 | ||||||||
• death of Anastasius I Dicorus | 9 July 518 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| History of the Byzantine Empire |
|---|
 |
| Preceding |
| Early period (330–717) |
| Middle period (717–1204) |
| Late period (1204–1453) |
| Timeline |
| By topic |
|
|
The Eastern Roman Empire was ruled by the Leonid dynasty from AD 457, the accession of Leo I, to 518, the death of Anastasius I. The rule of the Leonid dynasty coincided with the rapid decline, collapse and eventual fall of the Western Roman Empire. Following the end of the Western Empire, Emperor Zeno abolished the position of Western Roman Emperor and declared himself the sole Roman Emperor. The Eastern Roman Empire would come to last for several more centuries, and subsequent dynasties would invest large amounts of resources in attempts to retake the western provinces.
The Leonid dynasty also ruled the Western Roman Empire from 474 to its abolition in AD 480.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search
