
Back توزيع منتظم Arabic Distribución uniforme continua AST Раўнамернае непарыўнае размеркаванне Byelorussian সম-বিন্যাস (অবিচ্ছিন্ন) Bengali/Bangla Distribució uniforme contínua Catalan Rovnoměrné rozdělení Czech Татăлми пĕр тикĕс валеçӳ CV Ligefordeling Danish Stetige Gleichverteilung German Ομοιόμορφη κατανομή (συνεχής) Greek
| Continuous uniform | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Probability density function 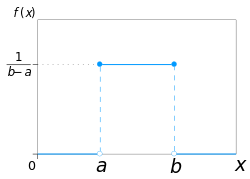 Using maximum convention | |||
|
Cumulative distribution function  | |||
| Notation | |||
| Parameters | |||
| Support | |||
| CDF | |||
| Mean | |||
| Median | |||
| Mode | |||
| Variance | |||
| MAD | |||
| Skewness | |||
| Excess kurtosis | |||
| Entropy | |||
| MGF | |||
| CF | |||
In probability theory and statistics, the continuous uniform distributions or rectangular distributions are a family of symmetric probability distributions. Such a distribution describes an experiment where there is an arbitrary outcome that lies between certain bounds.[1] The bounds are defined by the parameters, and which are the minimum and maximum values. The interval can either be closed (i.e. ) or open (i.e. ).[2] Therefore, the distribution is often abbreviated where stands for uniform distribution.[1] The difference between the bounds defines the interval length; all intervals of the same length on the distribution's support are equally probable. It is the maximum entropy probability distribution for a random variable under no constraint other than that it is contained in the distribution's support.[3]
- ^ a b Dekking, Michel (2005). A modern introduction to probability and statistics : understanding why and how. London, UK: Springer. pp. 60–61. ISBN 978-1-85233-896-1.
- ^ Walpole, Ronald; et al. (2012). Probability & Statistics for Engineers and Scientists. Boston, USA: Prentice Hall. pp. 171–172. ISBN 978-0-321-62911-1.
- ^ Park, Sung Y.; Bera, Anil K. (2009). "Maximum entropy autoregressive conditional heteroskedasticity model". Journal of Econometrics. 150 (2): 219–230. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.511.9750. doi:10.1016/j.jeconom.2008.12.014.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search
![{\displaystyle {\mathcal {U}}_{[a,b]}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/906b38f0905adef68e3c8c7ca6de15858f7742ce)

![{\displaystyle [a,b]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/9c4b788fc5c637e26ee98b45f89a5c08c85f7935)
![{\displaystyle {\begin{cases}{\frac {1}{b-a}}&{\text{for }}x\in [a,b]\\0&{\text{otherwise}}\end{cases}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/648692e002b720347c6c981aeec2a8cca7f4182f)
![{\displaystyle {\begin{cases}0&{\text{for }}x<a\\{\frac {x-a}{b-a}}&{\text{for }}x\in [a,b]\\1&{\text{for }}x>b\end{cases}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/2948c023c98e2478806980eb7f5a03810347a568)














