
Back Auflösungsgrenze German Córas díraonacháin theoranta Irish Diffraction limited Italian 回折限界 Japanese 회절 한계 Korean Diffractielimiet Dutch Limite de difração Portuguese Дифракционный предел Russian ขีดจำกัดการเลี้ยวเบน Thai Дифракційна межа Ukrainian

In optics, any optical instrument or system – a microscope, telescope, or camera – has a principal limit to its resolution due to the physics of diffraction. An optical instrument is said to be diffraction-limited if it has reached this limit of resolution performance. Other factors may affect an optical system's performance, such as lens imperfections or aberrations, but these are caused by errors in the manufacture or calculation of a lens, whereas the diffraction limit is the maximum resolution possible for a theoretically perfect, or ideal, optical system.[1]
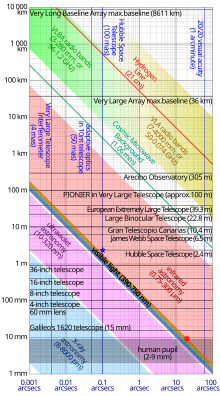
The diffraction-limited angular resolution, in radians, of an instrument is proportional to the wavelength of the light being observed, and inversely proportional to the diameter of its objective's entrance aperture. For telescopes with circular apertures, the size of the smallest feature in an image that is diffraction limited is the size of the Airy disk. As one decreases the size of the aperture of a telescopic lens, diffraction proportionately increases. At small apertures, such as f/22, most modern lenses are limited only by diffraction and not by aberrations or other imperfections in the construction.
For microscopic instruments, the diffraction-limited spatial resolution is proportional to the light wavelength, and to the numerical aperture of either the objective or the object illumination source, whichever is smaller.
In astronomy, a diffraction-limited observation is one that achieves the resolution of a theoretically ideal objective in the size of instrument used. However, most observations from Earth are seeing-limited due to atmospheric effects. Optical telescopes on the Earth work at a much lower resolution than the diffraction limit because of the distortion introduced by the passage of light through several kilometres of turbulent atmosphere. Advanced observatories have started using adaptive optics technology, resulting in greater image resolution for faint targets, but it is still difficult to reach the diffraction limit using adaptive optics.
Radio telescopes are frequently diffraction-limited, because the wavelengths they use (from millimeters to meters) are so long that the atmospheric distortion is negligible. Space-based telescopes (such as Hubble, or a number of non-optical telescopes) always work at their diffraction limit, if their design is free of optical aberration.
The beam from a laser with near-ideal beam propagation properties may be described as being diffraction-limited. A diffraction-limited laser beam, passed through diffraction-limited optics, will remain diffraction-limited, and will have a spatial or angular extent essentially equal to the resolution of the optics at the wavelength of the laser.
- ^ Born, Max; Emil Wolf (1997). Principles of Optics. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-63921-2.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search
