
Back Gljivni dimorfizam BS Dimorfisme fúngic Catalan Dimorfismo fúngico Spanish قارچهای دو ریخت Persian Dimorf gombák Hungarian 二形性真菌 Japanese Dimorf sopp NN Grzyby dymorficzne Polish Fungo dimórfico Portuguese Дріжджоподібні гриби Ukrainian
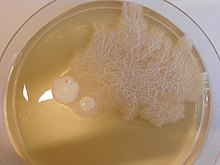
Dimorphic fungi are fungi that can exist in the form of both mold[1] and yeast. This is usually brought about by change in temperature and the fungi are also described as thermally dimorphic fungi.[2] An example is Talaromyces marneffei,[3] a human pathogen that grows as a mold at room temperature, and as a yeast at human body temperature.
The term dimorphic is commonly used for fungi that can grow both as yeast and filamentous cells, however many of these dimorphic fungi actually can grow in more than these two forms. Dimorphic is thus often used as a general reference for fungi being able to switch between yeast and filamentous cells, but not necessary limiting more shapes.[4][a]
- ^ "Fungi". Archived from the original on June 6, 2009. Retrieved 2009-06-06.
- ^ Gauthier, GM (May 2017). "Fungal Dimorphism and Virulence: Molecular Mechanisms for Temperature Adaptation, Immune Evasion, and In Vivo Survival". Mediators Inflamm. 2017: 8619307. doi:10.1155/2017/8619307. PMC 5463159. PMID 28626346.
- ^ Chandler JM, Treece ER, Trenary HR, et al. (2008). "Protein profiling of the dimorphic, pathogenic fungus, Penicillium marneffei". Proteome Sci. 6 (1): 17. doi:10.1186/1477-5956-6-17. PMC 2478645. PMID 18533041.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Kerridgewas invoked but never defined (see the help page).
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search