
Back ناهضات الدوبامين Arabic Agonista de la dopamina Catalan Dopaminagonist German آگونیست دوپامین Persian Agoniste de la dopamine French אגוניסטים לדופמין HE Agonisti dopaminergici Italian 도파민 작용제 Korean Agonista de dopamina Portuguese Dopaminski agonist Serbo-Croatian
| Dopamine agonist | |
|---|---|
| Drug class | |
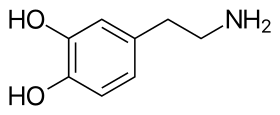 The skeletal structure of dopamine | |
| Class identifiers | |
| Use | Parkinson's disease, hyperprolactinemia, restless legs syndrome |
| ATC code | N04BC |
| Biological target | Dopamine receptors |
| External links | |
| MeSH | D010300 |
| Legal status | |
| In Wikidata | |
A dopamine agonist (DA) is a compound that activates dopamine receptors. There are two families of dopamine receptors, D1-like and D2-like. They are all G protein-coupled receptors. D1- and D5-receptors belong to the D1-like family and the D2-like family includes D2, D3 and D4 receptors.[1] Dopamine agonists are primarily used in the treatment of the motor symptoms of Parkinson's disease, and to a lesser extent, in hyperprolactinemia and restless legs syndrome.[2][3] They are also used off-label in the treatment of clinical depression. Impulse control disorders are associated with the use of dopamine agonists for whatever condition.[3]
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
:1was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
:5was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Spencer H, Anderton RS (2024). "Trait Impulsivity as a Feature of Parkinson's Disease Treatment and Progression". Parkinsons Dis. 2024: 8770997. doi:10.1155/2024/8770997. PMC 11102119. PMID 38766569.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search