Back Wei (estrella) AST Epsilon Scorpii German Wei (estrella) Spanish اپسیلون کژدم Persian Epsilon Scorpii French אפסילון בעקרב HE ऍप्सिलन स्कोर्पाए तारा Hindi Epsilon Scorpii ID Epsilon Scorpii Italian さそり座イプシロン星 Japanese
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
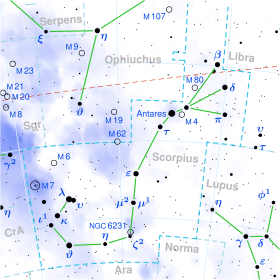
| Constellation | Scorpius |
| Right ascension | 16h 50m 09.8s[1] |
| Declination | –34° 17′ 36″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | +2.310[2] (2.24 - 2.35)[3]) |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | K1 III[4] |
| U−B color index | +1.147[2] |
| B−V color index | +1.150[2] |
| Variable type | suspected[3] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | –2.5[5] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: –614.85[1] mas/yr Dec.: –255.98[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 51.19 ± 0.22 mas[1] |
| Distance | 63.7 ± 0.3 ly (19.54 ± 0.08 pc)[1] |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | 0.78 ± 0.04[6] |
| Details[7] | |
| Mass | 1.4±0.1 M☉ |
| Radius | 15.5±0.5 R☉ |
| Luminosity | 53.7±0.6 L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 2.1±0.07 cgs |
| Temperature | 4583±125 K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | –0.17 dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 2.6 ± 0.5[8] km/s |
| Age | 3.92[9] Gyr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
Epsilon Scorpii (ε Scorpii, abbreviated Eps Sco, ε Sco), formally named Larawag /ˈlærəwæɡ/,[11] is a star in the southern zodiac constellation of Scorpius. It has an apparent visual magnitude of +2.3,[2] making it the fifth-brightest member of the constellation. Parallax measurements made during the Hipparcos mission provide an estimated distance to this star of around 63.7 light-years (19.5 parsecs) from the Sun.[1]
Epsilon Scorpii has a stellar classification of K1 III,[4] which indicates it has exhausted the supply of hydrogen at its core and evolved into a giant star. Currently, it has expanded to 15.5 times the Sun's size and is emitting 54 times its luminosity.[7] Presently it is generating energy through the nuclear fusion of helium at its core, which, considering the star's composition, places it along an evolutionary branch termed the red clump.[12] The star's outer atmosphere has an effective temperature of 4,580 K,[7] giving it the orange hue of a cool K-type star.
ε Scorpii is classified as a suspected variable star,[3] although a study of Hipparcos photometry showed a variation of no more than 0.01–0.02 magnitudes.[12] It is an X-ray source with a luminosity of (1.5–1.6) × 1027 erg s−1.[6][13]
- ^ a b c d e f g Cite error: The named reference
aaa474_2_653was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d Cite error: The named reference
apjs15_459was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c Cite error: The named reference
gcvswas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
aj132_1_161was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
scfswas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
aaa335_591was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c Cite error: The named reference
kallingerwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
aj135_3_892was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Luck2015was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
SIMBADwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Naming Stars". IAU.org. Retrieved 16 December 2017.
- ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
ba10_593was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
aaa352_217was invoked but never defined (see the help page).
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search