
Back مستقبل Fc Arabic Receptor Fc Catalan Fc receptor Czech Fc-Rezeptoren German Receptor Fc Spanish Récepteur Fc French Receptor de Fc Galician Fc受容体 Japanese Fc-рецептор Russian เอฟซี รีเซพเตอร์ Thai
| Immunoglobulin-like receptor | |
|---|---|
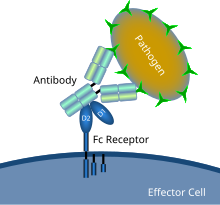 Schematic diagram showing Fc receptor interaction with an antibody-coated microbial pathogen | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | Fc receptor |
| Membranome | 10 |
In immunology, an Fc receptor is a protein found on the surface of certain cells – including, among others, B lymphocytes, follicular dendritic cells, natural killer cells, macrophages, neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, human platelets, and mast cells – that contribute to the protective functions of the immune system. Its name is derived from its binding specificity for a part of an antibody known as the Fc (fragment crystallizable) region. Fc receptors bind to antibodies that are attached to infected cells or invading pathogens. Their activity stimulates phagocytic or cytotoxic cells to destroy microbes, or infected cells by antibody-mediated phagocytosis or antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Some viruses such as flaviviruses use Fc receptors to help them infect cells, by a mechanism known as antibody-dependent enhancement of infection.[1]
- ^ Anderson R (2003). "Manipulation of cell surface macromolecules by flaviviruses". Advances in Virus Research. 59: 229–74. doi:10.1016/S0065-3527(03)59007-8. ISBN 9780120398591. PMC 7252169. PMID 14696331.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search