
Back خلل التنسج العضلي الليفي Arabic Fibromuskuläre Dysplasie German Displasia fibromuscular Spanish Dysplasie fibromusculaire French Displasia fibromuskular ID Displasia fibromuscolare Italian Dysplazja włóknisto-mięśniowa Polish Displasia fibromuscular Portuguese Фибромишићна дисплазија Serbian
| Fibromuscular dysplasia | |
|---|---|
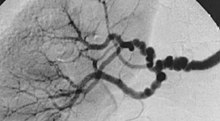 | |
| The "string-of-beads" feature in multi-focal fibromuscular dysplasia. The sign is caused by areas of relative stenoses alternating with small aneurysms. | |
| Specialty | Cardiology |
Fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD) is a non-atherosclerotic, non-inflammatory disease of the blood vessels that causes abnormal growth within the wall of an artery.[1] FMD has been found in nearly every arterial bed in the body, although the most commonly affected are the renal and carotid arteries.[1][2][3]
There are various types of FMD, with multi-focal fibroplasia being the most common. Less common forms of the disease include focal (previously known as intimal) and adventitial fibroplasia.[1][2][3][4] FMD predominantly affects middle-aged women, but it has been found in men and people of all ages.[1] Pediatric cases of FMD are vastly different from those of the adult population, and poorly studied. The prevalence of FMD is not known; although the disease was initially thought to be rare, some studies have suggested that it may be underdiagnosed.[5]
- ^ a b c d Poloskey SL, Olin JW, Mace P, Gornik HL (May 2012). "Fibromuscular dysplasia". Circulation. 125 (18): e636–9. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.090449. PMID 22566353.
- ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Olinwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Olin JW (April 2007). "Recognizing and managing fibromuscular dysplasia". Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine. 74 (4): 273–4, 277–82. doi:10.3949/ccjm.74.4.273. PMID 17438676. S2CID 21928728.
- ^ Olin JW, Sealove BA (March 2011). "Diagnosis, management, and future developments of fibromuscular dysplasia". Journal of Vascular Surgery. 53 (3): 826–36.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2010.10.066. PMID 21236620.
- ^ Hendricks NJ, Matsumoto AH, Angle JF, Baheti A, Sabri SS, Park AW, Stone JR, Patrie JT, Dworkin L, Cooper CJ, Murphy TP, Cutlip DE (October 2014). "Is fibromuscular dysplasia underdiagnosed? A comparison of the prevalence of FMD seen in CORAL trial participants versus a single institution population of renal donor candidates". Vasc Med. 19 (5): 363–7. doi:10.1177/1358863X14544715. PMID 25082538.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search