Back Formaldehied Afrikaans ميثانال Arabic Formaldehídu AST Formaldehid Azerbaijani فرمالدهید AZB Фармальдэгід Byelorussian Фармальдэгід BE-X-OLD Формалдехид Bulgarian ফরমালিন Bengali/Bangla Formaldehid BS
| |||
 | |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Formaldehyde[1] | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
Methanal[1] | |||
Other names
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 1209228 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.002 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| E number | E240 (preservatives) | ||
| 445 | |||
| KEGG | |||
| MeSH | Formaldehyde | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 2209 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties[7] | |||
| CH2O | |||
| Molar mass | 30.026 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless gas | ||
| Density | 0.8153 g/cm3 (−20 °C)[2] (liquid) | ||
| Melting point | −92 °C (−134 °F; 181 K) | ||
| Boiling point | −19 °C (−2 °F; 254 K)[2] | ||
| 400 g/L | |||
| log P | 0.350 | ||
| Vapor pressure | > 1 atm[3] | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 13.27 (hydrate)[4][5] | ||
| −18.6·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| 2.330 D[6] | |||
| Structure | |||
| C2v | |||
| Trigonal planar | |||
| Thermochemistry[8] | |||
Heat capacity (C)
|
35.387 J·mol−1·K−1 | ||
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
218.760 J·mol−1·K−1 | ||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−108.700 kJ·mol−1 | ||
Gibbs free energy (ΔfG⦵)
|
−102.667 kJ·mol−1 | ||
Std enthalpy of
combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
571 kJ·mol−1 | ||
| Pharmacology | |||
| QP53AX19 (WHO) | |||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
   [9] [9]
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H301+H311+H331, H314, H317, H335, H341, H350, H370[9] | |||
| P201, P280, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340+P310, P305+P351+P338, P308+P310[9] | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | 64 °C (147 °F; 337 K) | ||
| 430 °C (806 °F; 703 K) | |||
| Explosive limits | 7–73% | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
100 mg/kg (oral, rat)[12] | ||
LC50 (median concentration)
|
333 ppm (mouse, 2 h) 815 ppm (rat, 30 min)[13] | ||
LCLo (lowest published)
|
333 ppm (cat, 2 h)[13] | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 0.75 ppm ST 2 ppm (as formaldehyde and formalin)[10][11] | ||
REL (Recommended)
|
Ca TWA 0.016 ppm C 0.1 ppm [15-minute][10] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
Ca [20 ppm][10] | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | MSDS(Archived) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related aldehydes
|
|||
Related compounds
|
|||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
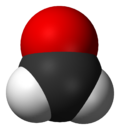
Formaldehyde (/fɔːrˈmældɪhaɪd/ ⓘ for-MAL-di-hide, US also /fər-/ ⓘ fər-) (systematic name methanal) is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH2O and structure H−CHO, more precisely H2C=O. The compound is a pungent, colourless gas that polymerises spontaneously into paraformaldehyde. It is stored as aqueous solutions (formalin), which consists mainly of the hydrate CH2(OH)2. It is the simplest of the aldehydes (R−CHO). As a precursor to many other materials and chemical compounds, in 2006 the global production of formaldehyde was estimated at 12 million tons per year.[14] It is mainly used in the production of industrial resins, e.g., for particle board and coatings.
Formaldehyde also occurs naturally. It is derived from the degradation of serine, dimethylglycine, and lipids. Demethylases act by converting N-methyl groups to formaldehyde.[15]
Formaldehyde is classified as a group 1 carcinogen[note 1][17] and can cause respiratory and skin irritation upon exposure.[16]
- ^ a b "Front Matter". Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 908. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ a b "SIDS Initial Assessment Report" (PDF). International Programme on Chemical Safety. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2019-03-28. Retrieved 2019-04-21.
- ^ Spence, Robert; Wild, William (1935). "114. The vapour-pressure curve of formaldehyde, and some related data". Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed): 506–509. doi:10.1039/jr9350000506.
- ^ "PubChem Compound Database; CID=712". National Center for Biotechnology Information. Archived from the original on 2019-04-12. Retrieved 2017-07-08.
- ^ "Acidity of aldehydes". Chemistry Stack Exchange. Archived from the original on 2018-09-01. Retrieved 2019-04-21.
- ^ Nelson, R. D. Jr.; Lide, D. R.; Maryott, A. A. (1967). "Selected Values of electric dipole moments for molecules in the gas phase (NSRDS-NBS10)" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2018-06-08. Retrieved 2019-04-21.
- ^ Weast, Robert C., ed. (1981). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (62nd ed.). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. pp. C–301, E–61. ISBN 0-8493-0462-8.
- ^ CRC handbook of chemistry and physics: a ready-reference book of chemical and physical data. William M. Haynes, David R. Lide, Thomas J. Bruno (2016-2017, 97th ed.). Boca Raton, Florida. 2016. ISBN 978-1-4987-5428-6. OCLC 930681942. Archived from the original on 2022-05-04. Retrieved 2022-04-12.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) CS1 maint: others (link) - ^ a b c Record of Formaldehyde in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, accessed on 13 March 2020.
- ^ a b c NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0293". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0294". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ "Substance Name: Formaldehyde [USP]". ChemlDplus. US National Library of Medicine. Archived from the original on 2017-09-18.
- ^ a b "Formaldehyde". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Humans, IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to (2006). Summary of Data Reported and Evaluation. International Agency for Research on Cancer. Archived from the original on 2024-02-02. Retrieved 2023-03-06.
- ^ Kamps, Jos J. A. G.; Hopkinson, Richard J.; Schofield, Christopher J.; Claridge, Timothy D. W. (2019). "How formaldehyde reacts with amino acids". Communications Chemistry. 2 (1): 126. Bibcode:2019CmChe...2..126K. doi:10.1038/s42004-019-0224-2.
- ^ a b "Formaldehyde and Cancer Risk". 10 June 2011. Archived from the original on 2023-09-20. Retrieved 2023-09-21.
- ^ Zhang, Luoping (2018). "CH 5. Formaldehyde Carcinogenesis". Formaldehyde: Exposure, Toxicity and Health Effects (1st ed.). Cambridge: Royal Society of Chemistry, The. ISBN 9781782629733.
Cite error: There are <ref group=note> tags on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=note}} template (see the help page).
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search