
Back Xeografía d'Antigua y Barbuda AST Геаграфія Антыгуа і Барбуды Byelorussian Geografía de Antigua y Barbuda Spanish جغرافیای آنتیگوآ و باربودا Persian Géographie d'Antigua-et-Barbuda French Geografia di Antigua e Barbuda Italian Antigvos ir Barbudos geografija Lithuanian Geografia Antigui i Barbudy Polish Geografia de Antígua e Barbuda Portuguese География Антигуа и Барбуды Russian
 | |
| Region | Caribbean |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 17°03′N 61°48′W / 17.050°N 61.800°W |
| Area | Ranked 181st |
| • Total | 442.6 km2 (170.9 sq mi) |
| • Land | 95.33% |
| • Water | 4.67% |
| Coastline | 153 km (95 mi) |
| Borders | No land borders |
| Highest point | Boggy Peak 402 meters (1,319 ft) |
| Lowest point | Atlantic Ocean 0 metres (0 ft) |
| Longest river | None |
| Largest lake | Potsworks Reservoir 2.430 ha (6.00 acres) |
| Terrain | low-lying limestone and coral islands, with some higher volcanic areas |
| Natural resources | marine resources, cotton |
| Natural hazards | hurricanes and tropical storms (July to October); periodic droughts |
| Environmental issues | water management, deforestation |
| Exclusive economic zone | 110,089 km2 (42,506 sq mi) |

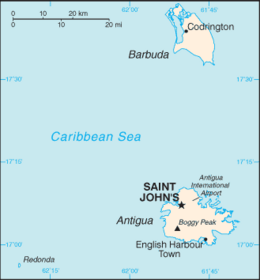
Antigua and Barbuda lie in the eastern arc of the Leeward Islands of the Lesser Antilles, separating the Atlantic Ocean from the Caribbean Sea.[1] Antigua is 650 km (400 mi) southeast of Puerto Rico; Barbuda lies 48 km (30 mi) due north of Antigua, and the uninhabited island of Redonda is 56 km (35 mi) southwest of Antigua.[1]
The largest island of Antigua, is 21 km (about a dozen miles) across and 281 km2 (about a hundred square miles) in area.[1] Barbuda covers 161 km2 (62 sq mi) while Redonda encompasses 2.6 km2 (1.0 sq mi).[1] The capital of Antigua and Barbuda is St. John's, located at St. John's Harbour on the northwest coast of Antigua.[1] The principal city of Barbuda is Codrington, located on Codrington Lagoon.[1]
- ^ a b c d e f Sturges-Vera, Karen (1987). "Antigua and Barbuda: Geography". In Meditz, Sandra W.; Hanratty, Dennis M. (eds.). Islands of the Commonwealth Caribbean: a regional study. Washington, D.C.: Federal Research Division, Library of Congress. pp. 435–437. OCLC 49361510.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.{{cite encyclopedia}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link)
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search