 | |
| Continent | Australia |
|---|---|
| Region | Southeast Australia |
| Coordinates | 37°31′S 149°58′E / 37.51°S 149.97°E — 33°58′S 140°58′E / 33.97°S 140.96°E |
| Area | Ranked 6th among states and territories |
| • Total | 227,444[2] km2 (87,817 sq mi) |
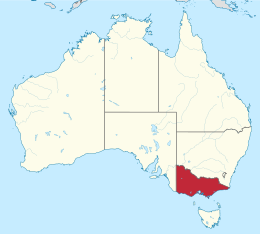
| Borders | Land borders: New South Wales, South Australia. Maritime Borders: Tasmania |
| Highest point | Mount Bogong 1,986 m (6,516 ft) |
| Lowest point | Bass Strait sea level |
| Longest river | Goulburn River 654 km (406 mi) |
| Largest lake | Gippsland Lakes 600 km² (373 sq mi) |
Victoria is the southernmost mainland state of Australia. With an area of 227,444 km2 (87,817 sq mi), it is Australia's sixth largest state/territory, comparable in size to the island of Great Britain or the U.S. state of Utah. It is bound to the northwest by South Australia, directly north by New South Wales, and also shares a maritime border with Tasmania across the Bass Strait to the south. Most of Victoria's northern border lies along the Murray River. The eastern half of the state is dominated by the Australian Alps and the surrounding highlands (plateaus and hills) of the Great Dividing Range, which also to a lesser extent extend far into the west of the state and ease off after The Grampians. By comparison the north and northwest of the state is extremely flat with little prominence.
Approximately 80% of Victoria's population lives around the coasts of the Port Phillip Bay and (to a lesser extent) Western Port Bay in the south-central region, chiefly in the state's two largest cities, Melbourne (state capital) and Geelong.
- ^ Jacaranda Atlas 6th Edition. Pages 80-87
- ^ https://www.ga.gov.au/scientific-topics/national-location-information/dimensions/area-of-australia-states-and-territories
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search
