
Back Heunenburg CEB Heuneburg German Heuneburg Esperanto هوینه بورگ Persian Heuneburg French Heuneburg Italian Heuneburg LB Heuneburg Dutch Heuneburg Polish Хойнебург Russian
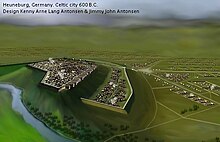 Reconstructed Celtic Heuneburg in 600 B.C. | |
Location in Baden-Württemberg | |
| Location | near Herbertingen, Baden-Württemberg |
|---|---|
| Region | Germany |
| Coordinates | 48°05′41″N 09°24′43″E / 48.09472°N 9.41194°E |
| Type | Hillfort, burial mounds |
| History | |
| Builder | Celts |
| Material | wood, earth |
| Founded | main structure 7th century BC |
| Abandoned | 5th century BC |
| Periods | Iron Age |
| Cultures | Celts, Hallstatt culture, La Tène (?) |
| Site notes | |
| Public access | Yes |
The Heuneburg is a prehistoric Celtic hillfort by the river Danube in Hundersingen near Herbertingen, between Ulm and Sigmaringen, Baden-Württemberg, in the south of Germany, close to the modern borders with Switzerland and Austria. It is considered to be one of the most important early Celtic centres in Central Europe, particularly during the Iron Age Hallstatt culture period. Apart from the fortified citadel, there are extensive remains of settlements and burial areas spanning several centuries.
The fortified citadel measures about 300 by 150 m (980 by 490 ft). It stood on a strategically positioned mountain spur that rises steeply 40 m (130 ft) above the Danube. It is at the centre of a fertile river plain, surrounded by rolling hill country. During the Iron Age the Heuneburg is thought to have controlled a surrounding area of over 1,000 km2 (390 sq mi) including other hilltop settlements, hamlets, villages, roads, cemeteries and cult or gathering places.[1]
The settlement has been called "oldest city north of the alps",[2][3][4] and has been identified with the Celtic city of Pyrene mentioned by Herodotus.[1][2]
..."The Istros river arises among the Celts and the polis of Pyrene, cutting Europe across the middle" — Herodotus (c.484–c.425 BC).[a]
- ^ a b Krause, Dirk (2020). "Earliest town north of the Alps. New excavations and research in the Heuneburg region". In Zamboni, Lorenzo (ed.). Crossing the Alps. Sidestone Press. pp. 299–314.
Recent excavations indicate that the Heuneburg controlled an area of over 1,000 km2 with cemeteries, further hilltop settlements, hamlets, villages, roads and cult or gathering places. It was not only the Heuneburg itself that must have formed an architectonically impressive agglomeration. Consequently, the polis Pyrene stands for this whole system, not just the hillfort of the Heuneburg.
- ^ a b "Heuneburg - Celtic city of Pyrene". heuneburg-pyrene.de.
- ^ "Heuneburg: Celtic town in Upper Swabia" (PDF).
- ^ Krause, Dirk; Fernández-Götz, Manuel (2012). "Heuneburg: First city north of the Alps". Current World Archaeology. 55: 28–34.
- ^ Roberts 2015, pp. 62.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search

