Khalji dynasty of Bengal | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE 1204–CE 1231 | |||||||||||||
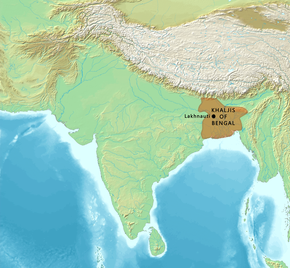
Location of the Khaljis of Bengal and neighbouring South Asian polities, circa 1230 CE.[1] | |||||||||||||
| Capital | Lakhnauti | ||||||||||||
| Common languages | Persian (official) Arabic (religious) | ||||||||||||
| Religion | Sunni Islam | ||||||||||||
| Government | Tribal oligarchy[2] | ||||||||||||
• 1204–1206 | Muhammad Bakhtiyar Khalji | ||||||||||||
• 1206–1208 | Muhammad Shiran Khalji | ||||||||||||
• 1208–1210 | Iwaz Khalji | ||||||||||||
• 1210–1212 | Ali Mardan Khalji | ||||||||||||
• 1212–1227 | Iwaz Khalji | ||||||||||||
• 1229–1230 | Dawlat Shah | ||||||||||||
• 1231 | Balka Khalji | ||||||||||||
| Historical era | Middle Kingdoms of India | ||||||||||||
• Established | CE 1204 | ||||||||||||
• Disestablished | CE 1231 | ||||||||||||
| Currency | Taka | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Today part of | Bangladesh India | ||||||||||||
The Khalji dynasty (Bengali: খলজি রাজবংশ, Persian: خاندان خلجی) was the first Muslim dynasty to rule Bengal. The dynasty, which hailed from the Garmsir region of present-day Afghanistan, was founded in 1204 by Muhammad Bakhtiyar Khalji, a Muslim Turko-Afghan[3][4] general of the Ghurid Empire.[5][6] The Khaljis initially pledged allegiance to Sultan Muhammad of Ghor until his death in 1206, though their rule in Bengal was mostly independent. Under the rule of Iwaz Khalji, Bengal experienced major developments such as its first naval force, flood defence systems and linkage with the Grand Trunk Road. The dynasty was based in the city of Lakhnauti in northern Bengal, later expanding eastwards and southwards. Nasiruddin Mahmud, the son of Mamluk sultan Iltutmish of Delhi managed to conquer Bengal in 1227; although the Khaljis briefly reasserted their independence, they surrendered to the Mamluks in 1231, who replaced them with a series of regional governors.
- ^ Schwartzberg, Joseph E. (1978). A Historical atlas of South Asia. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. p. 37, 147. ISBN 0226742210.
- ^ Know Your State West Bengal. Arihant Experts. 2019. p. 15.
Turk-Afghan Rule: Muhammad Bakhtiyar Khilji's invasion to Bengal marked the advent of Turk-Afghan rule in Bengal.
- ^ Chandra, Satish (2004). Medieval India: From Sultanat to the Mughals-Delhi Sultanat (1206–1526). p. 226.
Although the Afghans formed a large group in the army of the Delhi Sultanat, only few Afghan nobles had been accorded important positions. That is why Bakhtiyar Khalji who was part – Afghan had to seek his fortune in Bihar and Bengal.
- ^ Know Your State West Bengal. Arihant Experts. 2019. p. 15.
Turk-Afghan Rule: Muhammad Bakhtiyar Khilji's invasion to Bengal marked the advent of Turk-Afghan rule in Bengal.
- ^ Chandra, Satish (2004). Medieval India: From Sultanat to the Mughals-Delhi Sultanat (1206–1526). p. 226.
Although the Afghans formed a large group in the army of the Delhi Sultanat, only few Afghan nobles had been accorded important positions . That is why Bakhtiyar Khalji who was part – Afghan had to seek his fortune in Bihar and Bengal .
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search