
Back Indôchina ACE Indo-China Afrikaans इंडोचायना ANP جنوب شرق آسيا البري Arabic الصين الهنديه ARZ Indochina AST Hind-Çin Azerbaijani Һинд-Ҡытай Bashkir Indochina BAR Indotsina BCL
 | |
| Population | 243,201,036 (1 July 2019) |
|---|---|
| GDP (PPP) | $2.877 trillion (2021) |
| GDP (nominal) | $1.485 trillion (2022) |
| Countries | |
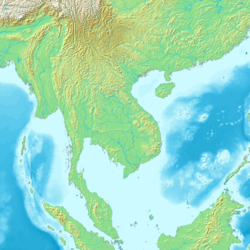
Mainland Southeast Asia (historically known as Indochina and the Indochinese Peninsula) is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the west and the Pacific Ocean to the east. It includes the countries of Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar, Singapore, Thailand and Vietnam as well as Peninsular Malaysia.[1]
The term Indochina (originally Indo-China) was coined in the early nineteenth century, emphasizing the historical cultural influence of Indian and Chinese civilizations on the area. The term was later adopted as the name of the colony of French Indochina (today's Cambodia, Laos, and Vietnam). Today, the term Mainland Southeast Asia is more commonly used, in contrast to Maritime Southeast Asia for the island groups off the coast of the peninsula.
- ^ "Southeast Asia". Britannica. Retrieved 8 April 2025.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search