
Back نورإبينفرين (دواء) Arabic Norepinefrina (medicación) Spanish Նորէպինեֆրին (դեղամիջոց) Armenian ନର୍ଏପିନେଫ୍ରିନ (ଔଷଧ) OR Norepinephrine (thuốc) Vietnamese 去甲基腎上腺素 (藥物) Chinese
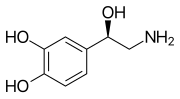 Skeletal formula of noradrenaline | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Levarterenol, Levophed, Norepin, other |
| Other names | Noradrenaline (R)-(–)-Norepinephrine l-1-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-2-aminoethanol |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Physiological data | |
| Source tissues | Locus coeruleus; sympathetic nervous system; adrenal medulla |
| Target tissues | System-wide |
| Receptors | α1, α2, β1, β3 |
| Agonists | Sympathomimetic drugs, clonidine, isoprenaline |
| Antagonists | Tricyclic antidepressants, Beta blockers, antipsychotics |
| Metabolism | MAO-A; COMT |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | MAO-A; COMT |
| Excretion | Urine (84–96%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C8H11NO3 |
| Molar mass | 169.180 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Density | 1.397±0.06 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 217 °C (423 °F) (decomposes) |
| Boiling point | 442.6 °C (828.7 °F) ±40.0°C |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Norepinephrine, also known as noradrenaline, is a medication used to treat people with very low blood pressure.[2] It is the typical medication used in sepsis if low blood pressure does not improve following intravenous fluids.[3] It is the same molecule as the hormone and neurotransmitter norepinephrine.[2] It is given by slow injection into a vein.[2]
Common side effects include headache, slow heart rate, and anxiety.[2] Other side effects include an irregular heartbeat.[2] If it leaks out of the vein at the site it is being given, norepinephrine can result in limb ischemia.[2] If leakage occurs the use of phentolamine in the area affected may improve outcomes.[2] Norepinephrine works by binding and activating alpha adrenergic receptors.[2]
Norepinephrine was discovered in 1946 and was approved for medical use in the United States in 1950.[2][4] It is available as a generic medication.[2]
- ^ Andersen AM (1975). "Structural studies of metabolic products of dopamine. IV. Crystal and molecular structure of (-)-noradrenaline". Acta Chemica Scandinavica. Series B. 29 (8): 871–876. doi:10.3891/acta.chem.scand.29b-0871. PMID 1202890.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "Norepinephrine Bitartrate". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 26 March 2017. Retrieved 26 March 2017.
- ^ Latifi R (2016). Surgical Decision Making: Beyond the Evidence Based Surgery. Springer. p. 67. ISBN 9783319298245. Archived from the original on 2017-03-27.
- ^ Encyclopedia of the Neurological Sciences. Academic Press. 2014. p. 224. ISBN 9780123851581. Archived from the original on 2017-03-27.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search