
Back الرؤية المحيطية Arabic Visió perifèrica Catalan Peripheres Sehen German Periferia vidkapablo Esperanto Vision périphérique French परिधीय दृष्टि Hindi Visione periferica Italian 주변시 Korean Visão periférica Portuguese Peripheral vision SIMPLE
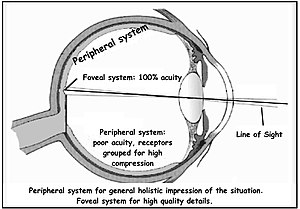


Peripheral vision, or indirect vision, is vision as it occurs outside the point of fixation, i.e. away from the center of gaze or, when viewed at large angles, in (or out of) the "corner of one's eye". The vast majority of the area in the visual field is included in the notion of peripheral vision. "Far peripheral" vision refers to the area at the edges of the visual field, "mid-peripheral" vision refers to medium eccentricities, and "near-peripheral", sometimes referred to as "para-central" vision, exists adjacent to the center of gaze.[1]
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search