
Back Fenoksimetielpenisillien Afrikaans فينوكسي ميثيل بنسيلين Arabic ফেনক্সিমিথাইলপেনিসিলিন Bengali/Bangla Fenoximetilpenicil·lina Catalan Phenoxymethylpenicillin Danish Phenoxymethylpenicillin German Fenoximetilpenicilina Spanish فنوکسیمتیلپنیسیلین Persian Fenoksimetyylipenisilliini Finnish Phénoxyméthylpénicilline French
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Veetids, Apocillin,[1] others |
| Other names | penicillin phenoxymethyl, penicillin V, penicillin VK |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a685015 |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 60% |
| Protein binding | 80% |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Elimination half-life | 30–60 min |
| Excretion | Kidney |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.566 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
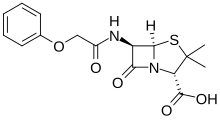
| Formula | C16H18N2O5S |
| Molar mass | 350.39 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 120–128 °C (248–262 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Phenoxymethylpenicillin, also known as penicillin V (PcV) and penicillin VK, is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections.[2] Specifically it is used for the treatment of strep throat, otitis media, and cellulitis.[2] It is also used to prevent rheumatic fever and to prevent infections following removal of the spleen.[2] It is given by mouth.[2]
Side effects include diarrhea, nausea, and allergic reactions including anaphylaxis.[2] It is not recommended in those with a history of penicillin allergy.[2] It is relatively safe for use during pregnancy.[3] It is in the penicillin and beta lactam family of medications.[4] It usually results in bacterial death.[4]
Phenoxymethylpenicillin was first made in 1948 by Eli Lilly.[5]: 121 It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[6] It is available as a generic medication.[4] In 2021, it was the 256th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 1 million prescriptions.[7][8]
- ^ "Apocillin". Felleskatalogen (in Norwegian). LMI (Legemiddelindustrien). Retrieved 23 June 2018.
fenoksymetylpenicillin
- ^ a b c d e f World Health Organization (2009). Stuart MC, Kouimtzi M, Hill SR (eds.). WHO Model Formulary 2008. World Health Organization. hdl:10665/44053. ISBN 9789241547659.
- ^ Hamilton R (2015). Tarascon Pocket Pharmacopoeia 2015 Deluxe Lab-Coat Edition. Jones & Bartlett Learning. p. 95. ISBN 9781284057560.
- ^ a b c "Penicillin V". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
- ^ Greenwood D (2008). "Wonder Drugs". Antimicrobial Drugs: Chronicle of a Twentieth Century Medical Triumph. OUP Oxford. ISBN 978-0-19-953484-5. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016.
- ^ World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- ^ "The Top 300 of 2021". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 15 January 2024. Retrieved 14 January 2024.
- ^ "Penicillin V - Drug Usage Statistics". ClinCalc. Retrieved 14 January 2024.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search