
Back بوابة:آسيا Arabic ܬܪܥܐ:ܐܣܝܐ ARC Portal:Asiya Azerbaijani Партал:Азія BE-X-OLD প্রবেশদ্বার:এশিয়া Bengali/Bangla دەروازە:ئاسیا CKB Portal:Asien German Portal:Asya DIQ Πύλη:Ασία Greek Portal:Asia Spanish

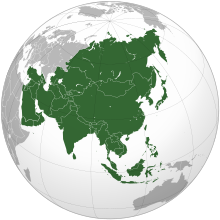 Asia (/ˈeɪʒə/ AY-zhə, UK also /ˈeɪʃə/ AY-shə) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometers, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which has long been home to the majority of the human population, was the site of many of the first civilizations. Its 4.7 billion people constitute roughly 60% of the world's population. Asia shares the landmass of Eurasia with Europe, and of Afro-Eurasia with both Europe and Africa. In general terms, it is bounded on the east by the Pacific Ocean, on the south by the Indian Ocean, and on the north by the Arctic Ocean. The border of Asia with Europe is a historical and cultural construct, as there is no clear physical and geographical separation between them. It is somewhat arbitrary and has moved since its first conception in classical antiquity. The division of Eurasia into two continents reflects East–West cultural, linguistic, and ethnic differences, some of which vary on a spectrum rather than with a sharp dividing line. A commonly accepted division places Asia to the east of the Suez Canal separating it from Africa; and to the east of the Turkish Straits, the Ural Mountains and Ural River, and to the south of the Caucasus Mountains and the Caspian and Black seas, separating it from Europe. China and India traded places as the largest economies in the world from 1 to 1800 CE. China was a major economic power for much of recorded history, with the highest GDP per capita until 1500. The Silk Road became the main east–west trading route in the Asian hinterlands while the Straits of Malacca stood as a major sea route. Asia has exhibited economic dynamism as well as robust population growth during the 20th century, but overall population growth has since fallen. Asia was the birthplace of most of the world's mainstream religions including Hinduism, Zoroastrianism, Judaism, Jainism, Buddhism, Confucianism, Taoism, Christianity, Islam, Sikhism, as well as many other religions. (Full article...) Featured articleMysore (/maɪˈsɔːr/ my-SOR), officially Mysuru (Kannada: [ˈmaɪˈsuːɾu] ), is the second-most populous city in the southern Indian state of Karnataka. It is the headquarters of Mysore district and Mysore division. As the traditional seat of the Wadiyar dynasty, the city functioned as the capital of the Kingdom of Mysore for almost six centuries (1399 to 1947). Known for its heritage structures, palaces (such as the famous Mysore Palace), and its culture, Mysore has been called the "City of Palaces", the "Heritage City", and the "Cultural Capital of Karnataka". It is one of the cleanest cities in India according to the Swachh Survekshan. Mysore is situated at the foothills of the Chamundi Hills. At an altitude of 770 m (2,530 ft) above mean sea level, the city of Mysore is geographically located at 12° 18′ 26″ north latitude and 76° 38′ 59″ east longitude. It is about 140 km (87.0 mi) southwest of the state's capital, Bangalore, and spreads across an area of 156 km2 (60 sq mi)(City + neighbouring census towns). The population of the city combined with its neighbouring towns in its metropolitan area is about 1,288,000 in 2023. (Full article...)Selected Country India, officially the Republic of India (ISO: Bhārat Gaṇarājya), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area; the most populous country as of June 2023; and from the time of its independence in 1947, the world's most populous democracy. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago. Their long occupation, initially in varying forms of isolation as hunter-gatherers, has made the region highly diverse, second only to Africa in human genetic diversity. Settled life emerged on the subcontinent in the western margins of the Indus river basin 9,000 years ago, evolving gradually into the Indus Valley Civilisation of the third millennium BCE. Between 2000 BCE and 1500 BCE, Indo-Aryans migrated into India from the northwest, bringing with them Sanskrit, an Indo-European language. Its evidence today is found in the hymns of the Rigveda. Preserved by an oral tradition that was resolutely vigilant, the Rigveda records the dawning of Hinduism in India. The Dravidian languages of India were supplanted in the northern and western regions. By 400 BCE, stratification and exclusion by caste had emerged within Hinduism, and Buddhism and Jainism had arisen, proclaiming social orders unlinked to heredity. Early political consolidations gave rise to the loose-knit Maurya and Gupta Empires based in the Ganges Basin. Their collective era was suffused with wide-ranging creativity, but also marked by the declining status of women, and the incorporation of untouchability into an organised system of belief. In South India, the Middle kingdoms exported Dravidian-languages scripts and religious cultures to the kingdoms of Southeast Asia. (Full article...)Featured biographyTiridates I (Parthian: 𐭕𐭉𐭓𐭉𐭃𐭕, Tīridāt; Ancient Greek: Τιριδάτης, Tiridátes) was King of Armenia beginning in 53 AD and the founder of the Arsacid dynasty of Armenia. The dates of his birth and death are unknown. His early reign was marked by a brief interruption towards the end of the year 54 and a much longer one from 58 to 63. In an agreement to resolve the Roman–Parthian conflict in and over Armenia, Tiridates I (one of the brothers of Vologases I of Parthia) was crowned king of Armenia by the Roman emperor Nero in 66; in the future, the king of Armenia was to be a Parthian prince, but his appointment required approval from the Romans. Even though this made Armenia a client kingdom, various contemporary Roman sources thought that Nero had de facto ceded Armenia to the Parthian Empire. In addition to being a king, Tiridates I was also a Zoroastrian priest and was accompanied by other magi on his journey to Rome in 66. In the early 20th century, Franz Cumont speculated that Tiridates was instrumental in the development of Mithraism which ultimately became the main religion of the Roman Army and spread across the whole empire. Furthermore, during his reign, he started reforming the administrative structure of Armenia, a reform which was continued by his successors, and which brought many Iranian customs and offices into it. (Full article...)General imagesThe following are images from various Asia-related articles on Wikipedia. Featured pictureThe head of a sandstone Buddha statue nestled in the tree roots beside the minor chapels of Wat Maha That, Phra Nakhon Si, Ayutthaya Province, Thailand. The temple is one of the most tourist and photographic attractions in the UNESCO World Heritage Site of Ayutthaya, an ancient capital of Siam.
Did you know...
Updated: 6:33, 14 February 2024 In the news
Related portalsMajor Religions in Asia Middle East Central Asia and Surroundings Indian Subcontinent Southeast Asia East Asia Selected panorama
The Hajj is an annual Islamic pilgrimage to Mecca, Saudi Arabia, the holiest city for Muslims, and a mandatory religious duty for Muslims that must be carried out at least once in their lifetime by all adult Muslims who are physically and financially capable of undertaking the journey, and can support their family during their absence. TopicsCategoriesAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
More portalsShortcuts to this page: Asia portal • P:ASIA Purge server cache |
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search






























































































