| Main Portal page | Indices | Projects |
 |
 |

| |
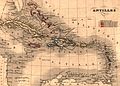
The Caribbean (/ˌkærɪˈbiːən, kəˈrɪbiən/ KARR-ib-EE-ən, kə-RIB-ee-ən, locally /ˈkærɪbiæn/ KARR-ib-ee-an; Spanish: el Caribe; French: les Caraïbes; Dutch: de Caraïben) is a subregion of the Americas that includes the Caribbean Sea and its islands, some of which are surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some of which border both the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean; the nearby coastal areas on the mainland are sometimes also included in the region. The region is south-east of the Gulf of Mexico and Northern America, east of Central America, and north of South America.
Situated largely on the Caribbean Plate, the region has thousands of islands, islets, reefs, and cays. Island arcs delineate the northern and eastern edges of the Caribbean Sea: the Greater Antilles in the north and the Lesser Antilles, which includes the Leeward Antilles, in the east and south. The nearby Lucayan Archipelago, comprising The Bahamas and the Turks and Caicos Islands, and the island of Barbados in the Lesser Antilles are considered to be a part of the Caribbean despite not bordering the Caribbean Sea. All the islands in the Antilles plus the Lucayan Archipelago form the West Indies, which is often interchangeable with the term Caribbean. On the mainland, Belize and the Caribbean coasts of Mexico, Central America, and South America, including the Yucatán Peninsula of Mexico, Bay Islands Department of Honduras, the North and South Caribbean Autonomous Regions of Nicaragua, the Limón Province of Costa Rica, the Archipelago of San Andrés, Providencia and Santa Catalina, Cartagena, and Barranquilla in Colombia, Maracaibo, Cumaná, and the Federal Dependencies in Venezuela, are also considered culturally Caribbean. French Guiana, Guyana, Panama, and Suriname are often included as parts of the Caribbean due to their political and cultural ties with the region.
Geopolitically, the islands of the Caribbean are often regarded as a subregion of North America, though sometimes they are included in Middle America or left as a subregion of their own; alternately, the term "Caribbean" may have the intended exclusion, or even unintentional inclusion, as part of Latin America. Generally the Caribbean area is organized into 33 political entities, including 13 sovereign states, 12 dependencies, historical disputed territories have existed, and seven other overseas territories. From 15 December 1954 to 10 October 2010, there was a territory known as the Netherlands Antilles composed of five islands, all of which were Dutch dependencies. From 3 January 1958 to 31 May 1962, there was also a short-lived political union called the British West Indies Federation composed of ten English-speaking Caribbean territories, all of which were then British dependencies. (Full article...)
Hurricane Dennis was a tropical cyclone that originated early in the Caribbean Sea and Gulf of Mexico during the record-breaking 2005 Atlantic hurricane season. The storm marked the fourth named storm, the second hurricane, and the first major hurricane of the season. Developing in July, it became the strongest Atlantic hurricane ever to form before August at that time. However, it held this title for only six days before being surpassed by Hurricane Emily. Additionally, Hurricane Dennis also became the second-wettest tropical cyclone in the state of Kentucky, second only to the 1960 Texas tropical storm.
Dennis originated from a tropical wave near Africa and intensified into a tropical depression by July 4 near the Windward Islands, crossing over Grenada. Strengthening further, it developed into a tropical storm before intensifying into a Category 1 hurricane by July 6, moving towards the Jamaica Channel. Rapidly intensifying into a Category 4 hurricane, Dennis made its first landfall in Granma Province, Cuba on July 8. After a period of weakening and subsequent re-intensification, Dennis reached its peak with winds of 150 mph before making its second landfall in Matanzas Province, Cuba on the same day. Weakening to a Category 1 hurricane, it intensified once more into a Category 4 hurricane, reaching a secondary peak with winds of 145 mph. On July 10, Dennis made landfall on Santa Rosa Island, Florida as a Category 3 hurricane before transitioning into an extratropical cyclone, which was later absorbed by another extratropical cyclone. (Full article...)Selected geography article -

Nassau (/ˈnæsɔː/ NASS-aw) is the capital and largest city of The Bahamas. It is located on the island of New Providence, which had a population of 246,329 in 2010, or just over 70% of the entire population of The Bahamas. As of April 2023, the preliminary results of the 2022 census of The Bahamas reported a population of 296,522 for New Providence, 74.26% of the country's population. Nassau is commonly defined as a primate city, dwarfing all other towns in the country. It is the centre of commerce, education, law, administration, and media of the country.
Lynden Pindling International Airport, the major airport for The Bahamas, is located about 16 km (9.9 mi) west of the city centre of Nassau, and has daily flights to and from major cities in Canada, the Caribbean, the United Kingdom and the United States. Nassau is the site of the House of Assembly and various judicial departments and was considered historically to be a stronghold of pirates. The city was named in honour of William III of England, Prince of Orange-Nassau. (Full article...)Selected fare or cuisine -

Did you know? -
- ...that the Soufrière Hills volcano is an active complex stratovolcano with many lava domes forming its summit on the Caribbean island of Montserrat?
- ...that Gaia is an arts centre in Havana, set up as a not-for-profit collaboration between Cuban and international artists?
- ...that former Hollywood star Maureen O'Hara lives on Beef Island, in the British Virgin Islands? And that her third husband, Charles Blair, died in 1978 when the engine of a Grumman Goose he was flying from St. Croix to St. Thomas in the U.S. Virgin Islands exploded?
Related portals
Wikiproject
The golden swallow (Tachycineta euchrysea) is a swallow endemic to the Caribbean island of Hispaniola (split between the Dominican Republic and Haiti) and was once native to Jamaica, but is now extirpated there. It is restricted to isolated montane forests that primarily consist of the Hispaniolan pine (Pinus occidentalis). This species is considered to be a vulnerable species by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). The exact cause of its extirpation from Jamaica is unknown, but likely factors include predation by introduced mammals and habitat loss, although the habitat loss theory is not supported by much evidence. The last sighting of the nominate subspecies was in Hardwar Gap (located on the boundary between Saint Andrew and Portland parishes), with three birds being seen on 8 June 1989.
A relatively small swallow, the Jamaican subspecies had bronze upperparts and bronze sides of the head. The ears and lores were duller and the forehead area was more green than bronze. The shoulders, back, rump, and uppertail-coverts were, on the other hand, a coppery-bronze colour. The lesser and median coverts were more coppery, with the greater and primary-wing-coverts more of a dusky green. The primaries, secondaries, and tail were a dusky bronze-green. The underparts were mostly white. The legs, feet, and irides were dark brown, and the bill was black. The female was similar, but with its breast, and occasionally throat and undertail-coverts, mottled grey-brown. The juvenile was also mottled-grey brown, and duller overall. The Hispaniolan subspecies, T. e. sclateri, is primarily differentiated by its more deeply forked tail, blue-green forehead and uppertail-coverts, and blue-black wings and tail. (Full article...)Selected image -

Voters queue to cast their vote during the Haitian general election, 2006
Selected music -

Rumba is a secular genre of Cuban music involving dance, percussion, and song. It originated in the northern regions of Cuba, mainly in urban Havana and Matanzas, during the late 19th century. It is based on African music and dance traditions, namely Abakuá and yuka, as well as the Spanish-based coros de clave. According to Argeliers León, rumba is one of the major "genre complexes" of Cuban music, and the term rumba complex is now commonly used by musicologists. This complex encompasses the three traditional forms of rumba (yambú, guaguancó and columbia), as well as their contemporary derivatives and other minor styles.
Traditionally performed by poor workers of African descent in streets and solares (courtyards), rumba remains one of Cuba's most characteristic forms of music and dance. Vocal improvisation, elaborate dancing and polyrhythmic drumming are the key components of all rumba styles. Cajones (wooden boxes) were used as drums until the early 20th century, when they were replaced by tumbadoras (conga drums). During the genre's recorded history, which began in the 1940s, there have been numerous successful rumba bands such as Los Papines, Los Muñequitos de Matanzas, Clave y Guaguancó, AfroCuba de Matanzas and Yoruba Andabo. (Full article...)General images
Caribbean topics
Categories
New articles
Rules | Match log | Results page (for watching) | Last updated: 2024-08-25 19:54 (UTC)
Note: The list display can now be customized by each user. See List display personalization for details.
- Edison Key (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ashlar (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-08-25, score: 16
- Amersham Arms (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Lewishhh (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2024-08-25, score: 16
- Asesina (Brytiago and Darell song) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 222 Georgi (talk · contribs · new pages (7)) started on 2024-08-25, score: 16
- Virgin Islands at the 2024 Summer Paralympics (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Waraka Saki (talk · contribs · new pages (30)) started on 2024-08-25, score: 16
- Trinidad and Tobago at the 2024 Summer Paralympics (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Waraka Saki (talk · contribs · new pages (30)) started on 2024-08-25, score: 16
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines at the 2024 Summer Paralympics (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Waraka Saki (talk · contribs · new pages (30)) started on 2024-08-25, score: 16
- Jamaica at the 2024 Summer Paralympics (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Waraka Saki (talk · contribs · new pages (30)) started on 2024-08-25, score: 16
- Barbados at the 2024 Summer Paralympics (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Waraka Saki (talk · contribs · new pages (30)) started on 2024-08-25, score: 16
- Haiti at the 2024 Summer Paralympics (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Waraka Saki (talk · contribs · new pages (30)) started on 2024-08-25, score: 16
- Isidre Fainé (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Kippelboy (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-08-25, score: 16
- Yzquierdo (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Roastedbeanz1 (talk · contribs · new pages (83)) started on 2024-08-25, score: 16
- Léotaud (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by David Eppstein (talk · contribs · new pages (33)) started on 2024-08-24, score: 16
- Bed Chem (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by MaranoFan (talk · contribs · new pages (19)) started on 2024-08-24, score: 16
- Macagual, Villa Clara (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by CubanoBoi (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-08-24, score: 16
- 2019 Judgments of the Supreme Court of the United Kingdom (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by DotCoder (talk · contribs · new pages (10)) started on 2024-08-24, score: 16
- Aruba at the 2024 Summer Paralympics (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Pancrino86 (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2024-08-24, score: 16
- West Indian cricket team in England in 2025 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Goodknowme (talk · contribs · new pages (14)) started on 2024-08-23, score: 16
- Faulty Towers The Dining Experience (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Liselladen (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-08-15, score: 16
- José Morales Lemus (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by EssNS (talk · contribs · new pages (10)) started on 2024-08-24, score: 16
- Slave-owning slaves (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ttocserp (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2024-08-24, score: 24
- 2024 BSN Finals (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by JeanetteMartin (talk · contribs · new pages (16)) started on 2024-08-24, score: 16
- Benoît Batraville (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Spymaster Cosades (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-08-24, score: 16
- Ceremonial roll call for the 2020 Democratic National Convention (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SecretName101 (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-08-23, score: 16
- Ceremonial roll call at the 2024 Democratic National Convention (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SecretName101 (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-08-23, score: 32
- The Wake (sculpture) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by No Swan So Fine (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-08-23, score: 16
- Guy de Saint-Gelais (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Sovietblobfish (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-08-23, score: 24
- Luis Peralta (baseball) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Yankees10 (talk · contribs · new pages (11)) started on 2024-08-23, score: 16
- West Indies women's cricket team in England in 2025 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Goodknowme (talk · contribs · new pages (14)) started on 2024-08-23, score: 16
- Taste (Sabrina Carpenter song) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by MaranoFan (talk · contribs · new pages (19)) started on 2024-08-21, score: 16
- Está Cabrón Ser Yo (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 222 Georgi (talk · contribs · new pages (7)) started on 2024-08-23, score: 16
- 2015 World Youth Championships in Athletics – Boys' long jump (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Stojan212 (talk · contribs · new pages (36)) started on 2024-08-23, score: 16
- Smith Augustin (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ueutyi (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-08-23, score: 32
- Dominique Dupuy (politician) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ueutyi (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-08-23, score: 16
- Greenwoodiella (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Tom Radulovich (talk · contribs · new pages (43)) started on 2024-08-23, score: 16
- Miguel Aldama (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by EssNS (talk · contribs · new pages (10)) started on 2024-08-23, score: 16
- List of Lambda Iota Tau chapters (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rublamb (talk · contribs · new pages (15)) started on 2024-08-22, score: 16
- Deaths in March 1986 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Drewsky1211 (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-08-22, score: 24
- Haiti–Poland relations (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Marcin 303 (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-08-22, score: 16
- List of The Young and the Restless characters introduced in the 2000s (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Bobby Cohn (talk · contribs · new pages (58)) started on 2024-08-22, score: 16
- List of The Young and the Restless characters introduced in the 1970s (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Bobby Cohn (talk · contribs · new pages (58)) started on 2024-08-22, score: 16
- Jacob Ruychaver (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Pinatyaimi (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-08-22, score: 16
- Miguel Jerónimo Gutiérrez (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by EssNS (talk · contribs · new pages (10)) started on 2024-08-22, score: 16
- List of people present at the Accession Council of Charles III (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Cantab12 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-08-22, score: 40
- Khurdad (son of Hurmuzd-Afarid) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by LouisAragon (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-08-21, score: 16
- Ralph de la Torre (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Thriley (talk · contribs · new pages (21)) started on 2024-08-19, score: 16
- Consejo de Expertos Electorales de Latinoamérica (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Boud (talk · contribs · new pages (7)) started on 2024-08-22, score: 16
- Economy of Republic of Cuba (1902–1959) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Kvng (talk · contribs · new pages (17)) started on 2024-08-22, score: 24
- Black mariners (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Bkissin (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2024-08-22, score: 16
- Diosa (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 222 Georgi (talk · contribs · new pages (7)) started on 2024-08-22, score: 32
- Mairis Briedis vs. Mike Perez (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Sam11333 (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-08-22, score: 16
- Notre-Dame-de-Bon-Secours (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SafariScribe (talk · contribs · new pages (110)) started on 2024-08-22, score: 32
- The Bahamas–Cuba relations (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Silvertide goldwaves (talk · contribs · new pages (31)) started on 2024-08-22, score: 48
- Cat Island, The Bahamas (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Silvertide goldwaves (talk · contribs · new pages (31)) started on 2024-08-22, score: 16
- 3rd Legislature of the Haitian Parliament (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by RayneVanDunem (talk · contribs · new pages (24)) started on 2024-08-22, score: 16
- 2nd Legislature of the Haitian Parliament (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by RayneVanDunem (talk · contribs · new pages (24)) started on 2024-08-22, score: 16
- Partners Mel and Jay (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rayhelm wiki (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2024-08-22, score: 16
- List of kidnappings: 1990–1999 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Tollens (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2024-08-22, score: 16
- Neil Ellis (bishop) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by TheLionHasSeen (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-08-22, score: 16
- 2021 Men's NORCECA Volleyball Championship squads (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Theo649 (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-08-22, score: 24
- Indo–Trinidadians and Tobagonians (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Reading Beans (talk · contribs · new pages (27)) started on 2024-08-22, score: 91
- Julio Brito (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Nonickillo (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-08-21, score: 24
- List of kidnappings: 1950–1979 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Tollens (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2024-08-21, score: 64
- Honorato del Castillo (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by EssNS (talk · contribs · new pages (10)) started on 2024-08-21, score: 16
- List of consular districts of the United States (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by RayneVanDunem (talk · contribs · new pages (24)) started on 2024-08-21, score: 184
- List of Atlantic tropical storms (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Hurricanehink (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-08-21, score: 120
- William M. Currie (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Tsc9i8 (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-08-21, score: 16
- Yunier Dorticos vs. Dmitry Kudryashov (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Sam11333 (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-08-21, score: 16
- Demetrio Quirós Weyler (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by EssNS (talk · contribs · new pages (10)) started on 2024-08-21, score: 16
- Auxilio Mutuo Hospital (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by JeanetteMartin (talk · contribs · new pages (16)) started on 2024-08-21, score: 16
- Mainville-Joseph Soulouque (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by RayneVanDunem (talk · contribs · new pages (24)) started on 2024-08-21, score: 16
- 1st Legislature of the Haitian Parliament (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by RayneVanDunem (talk · contribs · new pages (24)) started on 2024-08-21, score: 16
- 2024 Senior League World Series (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by RedSox39 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-08-21, score: 16
- Armando Johnson (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Cocu15 (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2024-08-21, score: 48
- 2023 Senior League World Series (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by RedSox39 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-08-21, score: 24
- Krenakia (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Tom Radulovich (talk · contribs · new pages (43)) started on 2024-08-21, score: 16
- Yordan Alvarez (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by JDDJS (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-08-20, score: 40
- Darnell Edge (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Mitrovica02 (talk · contribs · new pages (42)) started on 2024-08-20, score: 48
- List of Magnolia species (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Chaotic Enby (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-08-20, score: 40
- 1972 USA Indoor Track and Field Championships (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Habst (talk · contribs · new pages (126)) started on 2024-08-20, score: 16
- September 1978 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Mandsford (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-08-19, score: 24
- Arkell Jude-Boyd (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Microwave Anarchist (talk · contribs · new pages (7)) started on 2024-08-19, score: 16
- 2024–25 Georgia Bulldogs basketball team (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by KingSkyLord (talk · contribs · new pages (100)) started on 2024-08-12, score: 16
- 2024 Venezuelan political crisis (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SandyGeorgia (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-08-20, score: 24
- Belisario Grave de Peralta (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by EssNS (talk · contribs · new pages (10)) started on 2024-08-20, score: 16
- Madan Sara (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Smallchief (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-08-20, score: 16
- Maria Guadalupe Guzmán (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Shenaall (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-08-20, score: 24
- Nassau Container Port (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Silvertide goldwaves (talk · contribs · new pages (31)) started on 2024-08-20, score: 16
- Gustavia English (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by KennedyBroseguini (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-08-20, score: 91
- 45th Legislature of the Haitian Parliament (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by RayneVanDunem (talk · contribs · new pages (24)) started on 2024-08-20, score: 16
- 46th Legislature of the Haitian Parliament (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by RayneVanDunem (talk · contribs · new pages (24)) started on 2024-08-19, score: 16
- 47th Legislature of the Haitian Parliament (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by RayneVanDunem (talk · contribs · new pages (24)) started on 2024-08-19, score: 16
- 50th Legislature of the Haitian Parliament (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by RayneVanDunem (talk · contribs · new pages (24)) started on 2024-08-19, score: 40
- Vesconte Maggiolo Map (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Mcapdevila (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-08-18, score: 16
- Maria Rodriguez Denton (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SigurdsSister (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-08-19, score: 16
- 1980 Riohacha TAC Caravelle crash (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Jay D. Easy (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-08-19, score: 16
- List of female winners of open chess tournaments (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Sportsfan77777 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-08-19, score: 16
- 2024 Intermediate League World Series (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Stan394 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-08-19, score: 16
- Klistan Lawrence (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Theo649 (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-08-18, score: 32
- Pierre François Sildor (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Cheney123 (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-08-18, score: 16
- Alfredo Brito (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Nonickillo (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-08-18, score: 16
- 2024 Women's Pan-American Volleyball Cup (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Thiago89 (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-08-18, score: 24
- Winsome Sinclair (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by PootisHeavy (talk · contribs · new pages (17)) started on 2024-08-18, score: 16
- List of Virgin Islands Legislatures (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by M2545 (talk · contribs · new pages (85)) started on 2024-08-18, score: 16
- Map of Viscount Maggiolo (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Mcapdevila (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-08-18, score: 16
- Hurricane Ernesto (2024) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Shmego (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-08-13, score: 155
- Robert Scarlett (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Tassedethe (talk · contribs · new pages (382)) started on 2024-08-18, score: 16
- Lollipop (Darell song) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 222 Georgi (talk · contribs · new pages (7)) started on 2024-08-18, score: 24
- Rigoberto Ramos (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SovietGGPT (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-08-18, score: 16
- Iglesia Parroquial Mayor del Espíritu Santo (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by EssNS (talk · contribs · new pages (10)) started on 2024-08-18, score: 16
- Roberto Vera Monroig (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SovietGGPT (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-08-18, score: 16
- Galapa, Colombia (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Castncoot (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2024-08-18, score: 16
- Atis Indepandan (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Spymaster Cosades (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-08-18, score: 16
- Andrés Manuel Sánchez (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by EssNS (talk · contribs · new pages (10)) started on 2024-08-17, score: 24
- Agenodesmus reticulatus (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by HCUPa (talk · contribs · new pages (11)) started on 2024-08-17, score: 56
- José Francisco Lemus (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by EssNS (talk · contribs · new pages (10)) started on 2024-08-17, score: 16
- Mario Brooks (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Avengers350 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-08-09, score: 24
- Robert Haynes (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Tassedethe (talk · contribs · new pages (382)) started on 2024-08-17, score: 16
- Sabana, Villa Clara (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by CubanoBoi (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-08-17, score: 16
- Donato Mármol (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by EssNS (talk · contribs · new pages (10)) started on 2024-08-17, score: 16
- Dan MacIntyre (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Tassedethe (talk · contribs · new pages (382)) started on 2024-08-17, score: 16
- Joe White (singer) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Karl Twist (talk · contribs · new pages (14)) started on 2024-08-17, score: 24
- 2015 World Youth Championships in Athletics – Boys' 400 metres hurdles (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Stojan212 (talk · contribs · new pages (36)) started on 2024-08-17, score: 16
- Puducherry diaspora (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Hemant Dabral (talk · contribs · new pages (77)) started on 2024-08-17, score: 56
- Cavan Sullivan (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by GiantSnowman (talk · contribs · new pages (27)) started on 2024-08-17, score: 16
- Helena Montalban (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by JeanetteMartin (talk · contribs · new pages (16)) started on 2024-08-17, score: 48
- Latin American Cities by GDP (PPP) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by AviationLover27 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-08-17, score: 27
- Agege bread (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by AKeen (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-08-17, score: 16
- List of ships built by Harland & Wolff (1859–1929) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by BarrelProof (talk · contribs · new pages (67)) started on 2024-08-17, score: 16
- Honduran–Guatemalan War (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by BarrelProof (talk · contribs · new pages (67)) started on 2024-08-16, score: 16
- Carta Vieja Yankees (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Captain Parmenter (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-08-16, score: 32
- List of legislatures of the Haitian Parliament (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by RayneVanDunem (talk · contribs · new pages (24)) started on 2024-08-16, score: 16
- Stéphane Vincent (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Masstic (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-08-16, score: 16
- Duberry (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SparklessPlug (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-08-16, score: 16
- Indo–Saint Lucians (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Hyphenation Expert (talk · contribs · new pages (47)) started on 2024-08-16, score: 91
- 23 Preguntas (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 222 Georgi (talk · contribs · new pages (7)) started on 2024-08-16, score: 16
- Shaquan Davis (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by BilledMammal (talk · contribs · new pages (14)) started on 2024-08-16, score: 16
- Pedro de Zúñiga y de la Cueva (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Xegma (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-08-16, score: 16
- Jose Abreu (basketball) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by JeanetteMartin (talk · contribs · new pages (16)) started on 2024-08-16, score: 16
- Nivia Fernández Hernández (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by TJMSmith (talk · contribs · new pages (27)) started on 2024-08-16, score: 16
- José María Caminero (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by BlkGeneral2000 (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2024-08-16, score: 56
- Andris Riché (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Cheney123 (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-08-15, score: 16
- Rodolphe Joazile (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Cheney123 (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-08-15, score: 16
- Simon Dieuseul Desras (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Cheney123 (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-08-15, score: 16
- List of official overseas trips made by Edward VIII (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Sinowinston (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-08-15, score: 48
- Arsenal de San Juan (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ligocsicnarf89 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-08-15, score: 16
- 1892–1896 Mississippi Legislature (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Globg (talk · contribs · new pages (24)) started on 2024-08-09, score: 16
- Maria Petra Giordano (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by JB Hoang Tam 2 (talk · contribs · new pages (10)) started on 2024-08-15, score: 16
- The Bitcoin Standard (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Cagliost (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-08-15, score: 16
- 2023 Men's NORCECA Volleyball Championship squads (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Theo649 (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-08-15, score: 24
- Eugènie Herlaar (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rigg (talk · contribs · new pages (9)) started on 2024-08-15, score: 16
- Abner Green (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Jengod (talk · contribs · new pages (34)) started on 2024-08-15, score: 32
- Portuguese Trinidadians and Tobagonians (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Sendo79 (talk · contribs · new pages (15)) started on 2024-08-15, score: 32
- Japanese Caribbean people (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Sendo79 (talk · contribs · new pages (15)) started on 2024-08-14, score: 75
- USAT Logan (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Jordanroderick (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-08-14, score: 48
- Benjamin F. McAdoo (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Generalissima (talk · contribs · new pages (86)) started on 2024-08-09, score: 16
- 2025 PGA Tour (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ajthom90 (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-08-14, score: 16
- Joseph-David de Barquier (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by BlkGeneral2000 (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2024-08-14, score: 32
- R&G (disambiguation) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Queen of Hearts (talk · contribs · new pages (11)) started on 2024-08-14, score: 16
- 2024 MTV MIAW Awards (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by JuliánLeiva66 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-08-13, score: 16
- Orlando Ribalta (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Stonecold415 (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-08-13, score: 16
- Luis T. Hernandez Terrazas (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by RaidingTraider54 (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-08-08, score: 16
- Belén Funes (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Bearcat (talk · contribs · new pages (80)) started on 2024-08-13, score: 16
- Puerto Rico Register of Historic Sites and Zones (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ligocsicnarf89 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-08-13, score: 16
- Andre Raymond (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Das osmnezz (talk · contribs · new pages (28)) started on 2024-08-13, score: 24
- Battle of Guayacanes (1863) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by BlkGeneral2000 (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2024-08-13, score: 16
- LIAT20 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by CROIX (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-08-13, score: 32
- Spanish Republican exiles (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by TheTastyWord (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-08-13, score: 16
- 2024–25 Virginia Cavaliers men's basketball team (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Swimmer33 (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2024-08-12, score: 36
- Saba Goglichidze (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Das osmnezz (talk · contribs · new pages (28)) started on 2024-08-12, score: 16
- Tilden Santiago (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Fixer88 (talk · contribs · new pages (33)) started on 2024-08-12, score: 16
- Meteorological history of Hurricane Sally (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Mariacallas2024 (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2024-08-12, score: 32
- Hipólito Marcano (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ivan Quiles (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-08-12, score: 16
- Historic Sanctuary of Machu Picchu (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by JustEMV (talk · contribs · new pages (24)) started on 2024-08-12, score: 16
- Fanus (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Duckmather (talk · contribs · new pages (64)) started on 2024-08-12, score: 16
- Segovia Registration Scandal (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by BlkGeneral2000 (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2024-08-12, score: 16
- Antonio María Segovia (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by BlkGeneral2000 (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2024-08-12, score: 48
- Dile Que Tú Me Quieres (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Floppykart (talk · contribs · new pages (7)) started on 2024-08-12, score: 16
- Wrexham A.F.C. Player of the Season (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Andre666 (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-08-12, score: 16
- Iris Hall (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Gamaliel (talk · contribs · new pages (23)) started on 2024-08-12, score: 16
- Battle of Jura (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by BlkGeneral2000 (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2024-08-12, score: 16
- List of Wrexham A.F.C. players (1–24 appearances) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Andre666 (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-08-12, score: 40
- List of Wrexham A.F.C. players (25–99 appearances) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Andre666 (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-08-12, score: 32
- Leandro Manzueta (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by BlkGeneral2000 (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2024-08-12, score: 16
- Eusebio Manzueta (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by BlkGeneral2000 (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2024-08-12, score: 28
- Freeport Container Port (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Silvertide goldwaves (talk · contribs · new pages (31)) started on 2024-08-12, score: 16
- Battle of Sabana de San Pedro (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by BlkGeneral2000 (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2024-08-12, score: 28
- Aquilino Gonell (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Atubofsilverware (talk · contribs · new pages (10)) started on 2024-08-12, score: 16
- Battle of La Canela (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by BlkGeneral2000 (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2024-08-12, score: 16
- Anthony Maldonado (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by KingSkyLord (talk · contribs · new pages (100)) started on 2024-08-12, score: 16
- Battle of Paso del Muerto (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by BlkGeneral2000 (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2024-08-12, score: 16
- List of Pershing Rifles units (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rublamb (talk · contribs · new pages (15)) started on 2024-08-12, score: 16
- Desirade (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 64.229.88.34 (talk · contribs · new pages (32)) started on 2024-08-11, score: 32
- La Llevo al Cielo (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 222 Georgi (talk · contribs · new pages (7)) started on 2024-08-11, score: 24
- Christopher Wormeley (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Tassedethe (talk · contribs · new pages (382)) started on 2024-08-11, score: 16
- 1996 USA Indoor Track and Field Championships (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Habst (talk · contribs · new pages (126)) started on 2024-08-11, score: 16
- Donnie Freeman (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Saizo7 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-08-11, score: 16
- MTV Hits (European TV channel) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by LDM2003 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-08-11, score: 32
- 2023 Junior League World Series (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by TomatoSandwich10 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-08-11, score: 16
- Battle of Arroyo Bermejo (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by BlkGeneral2000 (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2024-08-11, score: 72
- Mariah Pérez (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Mlodymmiastem (talk · contribs · new pages (17)) started on 2024-08-06, score: 32
- 2024 Summer Olympics closing ceremony flag bearers (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by CodyRhodesDiva (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-08-04, score: 64
- Mario Pabon (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by JeanetteMartin (talk · contribs · new pages (16)) started on 2024-08-10, score: 52
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
Shortcuts to this page: Portal:West Indies • P:CARIB Purge server cache
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search