Back بوابة:إنترنت Arabic دەروازە:ئینتەرنێت CKB Portál:Internet Czech Portal:Internet German Portal:Internet Spanish درگاه:اینترنت Persian Portail:Internet French פורטל:אינטרנט HE Պորտալ:Համացանց Armenian Portal:Internet ID
The Internet PortalThe Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a network of networks that consists of private, public, academic, business, and government networks of local to global scope, linked by a broad array of electronic, wireless, and optical networking technologies. The Internet carries a vast range of information resources and services, such as the interlinked hypertext documents and applications of the World Wide Web (WWW), electronic mail, telephony, and file sharing. The origins of the Internet date back to research that enabled the time-sharing of computer resources and the development of packet switching in the 1960s. The set of rules (communication protocols) to enable internetworking on the Internet arose from research and development commissioned in the 1970s by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) of the United States Department of Defense in collaboration with universities and researchers across the United States and in the United Kingdom and France. The ARPANET initially served as a backbone for the interconnection of regional academic and military networks in the United States to enable resource sharing. The funding of the National Science Foundation Network as a new backbone in the 1980s, as well as private funding for other commercial extensions, encouraged worldwide participation in the development of new networking technologies and the merger of many networks using DARPA's Internet protocol suite. The linking of commercial networks and enterprises by the early 1990s, as well as the advent of the World Wide Web, marked the beginning of the transition to the modern Internet, and generated sustained exponential growth as generations of institutional, personal, and mobile computers were connected to the network. Although the Internet was widely used by academia in the 1980s, the subsequent commercialization in the 1990s and beyond incorporated its services and technologies into virtually every aspect of modern life. (Full article...) Selected articleThe Signpost (formerly The Wikipedia Signpost) is the English Wikipedia's online newspaper. Managed by the volunteer community, it is published online with contributions from Wikimedia editors. The newspaper's scope includes the Wikimedia community and events related to Wikipedia, including Arbitration Committee rulings, Wikimedia Foundation issues, and other Wikipedia-related projects. It was founded in January 2005 by Wikipedian Michael Snow, who continued as a contributor until his February 2008 appointment to the Wikimedia Foundation's Board of Trustees. Former editor-in-chief The ed17 noted that during his tenure, from 2012 to 2015, the publication expanded its scope to report on the wider Wikimedia movement in addition to Wikipedia and its community. After it reported on the changes to European freedom of panorama law in June 2015, a number of publications referred to The Signpost for further information. (Full article...) Selected picture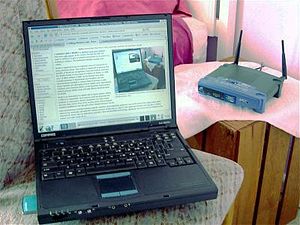 A wireless LAN or WLAN is a wireless local area network, which is the linking of two or more computers without using wires. WLAN utilizes spread-spectrum or OFDM modulation technology based on radio waves to enable communication between devices in a limited area, also known as the basic service set. This gives users the mobility to move around within a broad coverage area and still be connected to the network. News
Wikinews Internet portal
WikiProjects
Did you know (auto-generated) -
Selected biography
Vannevar Bush (March 11, 1890 – June 30, 1974) was an American engineer and science administrator, known for his work on analog computing, his political role in the development of the atomic bomb, and the idea of the memex—seen as a pioneering concept for the World Wide Web. A leading figure in the development of the military–industrial complex and the military funding of science in the United States, Bush was a prominent policymaker and public intellectual ("the patron saint of American science") during World War II and the ensuing Cold War. Through his public career, Bush was a proponent of democratic technocracy and of the centrality of technological innovation and entrepreneurship for both economic and geopolitical security.
General images -The following are images from various internet-related articles on Wikipedia.
Selected quoteMore Did you know...
Main topics
Featured contentCategoriesRelated portalsThings you can do
Associated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Wikipedia's portals |
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search