
Back بوابة:الأعاصير المدارية Arabic Portal:Ciclons tropicals Catalan Portal:Ciclones tropicales Spanish 포털:태풍 Korean Portaal:Tropische cyclonen Dutch Portal:Ciclones tropicais Portuguese สถานีย่อย:พายุหมุนเขตร้อน Thai Portal:熱帶氣旋 Chinese
The Tropical Cyclones Portal

A tropical cyclone is a storm system characterized by a large low-pressure center, a closed low-level circulation and a spiral arrangement of numerous thunderstorms that produce strong winds and heavy rainfall. Tropical cyclones feed on the heat released when moist air rises, resulting in condensation of water vapor contained in the moist air. They are fueled by a different heat mechanism than other cyclonic windstorms such as Nor'easters, European windstorms and polar lows, leading to their classification as "warm core" storm systems. Most tropical cyclones originate in the doldrums, approximately ten degrees from the Equator.
The term "tropical" refers to both the geographic origin of these systems, which form almost exclusively in tropical regions of the globe, as well as to their formation in maritime tropical air masses. The term "cyclone" refers to such storms' cyclonic nature, with anticlockwise rotation in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise rotation in the Southern Hemisphere. Depending on its location and intensity, a tropical cyclone may be referred to by names such as "hurricane", "typhoon", "tropical storm", "cyclonic storm", "tropical depression" or simply "cyclone".
Types of cyclone: 1. A "Typhoon" is a tropical cyclone located in the North-west Pacific Ocean which has the most cyclonic activity and storms occur year-round. 2. A "Hurricane" is also a tropical cyclone located at the North Atlantic Ocean or North-east Pacific Ocean which have an average storm activity and storms typically form between May 15 and November 30. 3. A "Cyclone" is a tropical cyclone that occurs in the South Pacific and Indian Oceans.
Selected named cyclone -
Hurricane Barry was an asymmetrical Category 1 hurricane that was the wettest tropical cyclone on record in Arkansas and the fourth-wettest in Louisiana. The second tropical or subtropical storm and first hurricane of the 2019 Atlantic hurricane season, Barry originated as a mesoscale convective vortex over southwestern Kansas on July 2. The system eventually emerged into the Gulf of Mexico from the Florida Panhandle on July 10, whereupon the National Hurricane Center (NHC) designated it as a potential tropical cyclone. Early on July 11, the system developed into a tropical depression, and strengthened into a tropical storm later that day. Dry air and wind shear caused most of the convection, or thunderstorms, to be displaced south of the center. Nevertheless, Barry gradually intensified. On July 13, Barry attained its peak intensity as Category 1 hurricane with 1-minute sustained winds of 75 mph (120 km/h) and a minimum central pressure of 993 millibars (29.3 inHg). At 15:00 UTC, Barry made its first landfall at Marsh Island, and another landfall in Intracoastal City, Louisiana, both times as a Category 1 hurricane. Barry quickly weakened after landfall, falling to tropical depression status on July 15. The storm finally degenerated into a remnant low over northern Arkansas on the same day, subsequently opening up into a trough on July 16. The storm's remnants persisted for another few days, while continuing its eastward motion, before being absorbed into another frontal storm to the south of Nova Scotia on July 19.
Barry was one of four hurricanes to strike Louisiana as a Category 1 hurricane in the month of July, the others being Bob in 1979, Danny in 1997, and Cindy in 2005. Numerous tropical storm watches and warnings were issued for Mississippi and Louisiana ahead of the storm. Several states declared state of emergencies ahead of the storm. Though Barry only produced hurricane-force winds in a small area of Louisiana, more than 153,000 customers lost power in the state. As Barry drifted westward over the Gulf of Mexico, storm surge caused widespread coastal flooding in Alabama, Mississippi, and Alabama. The storm's large circulation produced heavy rainfall over a large area, reaching 23.43 in (595 mm) near Ragley, Louisiana, and 16.59 in (421 mm) near Dierks, Arkansas. The latter value was the highest amount of rainfall recorded in Arkansas related to a tropical cyclone. Many roads, including Interstate highways, were flooded. Dozens of water rescues were carried out in Louisiana and Arkansas, where the most significant flooding occurred. In parts of the Northeastern United States and Ontario, Canada, severe thunderstorms from Barry's remnants caused an additional 160,000 power outages and spawned a few weak tornadoes. The storm caused two fatalities: one in Florida from rip currents, and one in Connecticut from fallen trees and wires. Damage from Barry was estimated to be about $900 million (2019 USD). (Full article...)Selected article -

The history of Atlantic tropical cyclone warnings details the progress of tropical cyclone warnings in the North Atlantic Ocean. The first service was set up in the 1870s from Cuba with the work of Father Benito Viñes. After his death, hurricane warning services were assumed by the US Army Signal Corps and United States Weather Bureau over the next few decades, first based in Jamaica and Cuba before shifting to Washington, D.C. The central office in Washington, which would evolve into the National Meteorological Center and the Weather Prediction Center, assumed the responsibilities by the early 20th century. This responsibility passed to regional hurricane offices in 1935, and the concept of the Atlantic hurricane season was established to keep a vigilant lookout for tropical cyclones during certain times of the year. Hurricane advisories issued every 12 hours by the regional hurricane offices began at this time.
The National Hurricane Center became a tropical cyclone warning center in 1956 and assumed many of the functions it has today by 1965. The National Hurricane Research Project, begun in the 1950s, used aircraft to study tropical cyclones and carry out experiments on mature hurricanes through its Stormfury project. Forecasts within the hurricane advisories were issued one day into the future in 1954 before being extended to two days into the future in 1961, three days into the future in 1964, and five days into the future in 2001. From the 1960s through the 1980s, work from the various regional hurricane offices was consolidated into the National Hurricane Center. Its name was changed to the Tropical Prediction Center in 1995, before reassuming its National Hurricane Center name in 2010. Tropical cyclone forecasting is done nowadays using statistical methods based on tropical cyclone climatology, as well as methods of numerical weather prediction where computers use mathematical equations of motion to determine their movement. (Full article...)Selected image -

Selected season -

The 2019 Atlantic hurricane season was the fourth consecutive above-average and damaging season dating back to 2016. The season featured eighteen named storms, however, many storms were weak and short-lived, especially towards the end of the season. Six of those named storms achieved hurricane status, while three intensified into major hurricanes. Two storms became Category 5 hurricanes, marking the fourth consecutive season with at least one Category 5 hurricane, the third consecutive season to feature at least one storm making landfall at Category 5 intensity, and the seventh on record to have multiple tropical cyclones reaching Category 5 strength. The season officially began on June 1 and ended on November 30. These dates historically describe the period each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin and are adopted by convention. However, tropical cyclogenesis is possible at any time of the year, as demonstrated by the formation of Subtropical Storm Andrea on May 20, making this the fifth consecutive year in which a tropical or subtropical cyclone developed outside of the official season.
The season's first hurricane, Barry, formed in mid-July in the northern Gulf of Mexico and struck Louisiana. Barry caused two deaths and produced flooding in Arkansas, Alabama, Louisiana, and Mississippi, with damage totaling about $600 million (2019 USD). Hurricane Dorian, the most intense tropical cyclone of the season, proved to be the costliest natural disaster in the history of the Bahamas, becoming the strongest hurricane to strike the country. Overall, Dorian caused about $5.1 billion in damage and 84 fatalities, mostly in the Bahamas. The 2019 season was the record fourth consecutive season to feature at least one Category 5 hurricane. Tropical Storm Fernand left flooding in Mexico, with approximately $11.3 million in damage and one death. Hurricane Humberto produced extensive damage in Bermuda, totaling at least $25 million. (Full article...)Related portals
Currently active tropical cyclones

Italicized basins are unofficial.
- North Atlantic (2024)
- No active systems
- East and Central Pacific (2024)
- No active systems
- West Pacific (2024)
- No active systems
- North Indian Ocean (2024)
- No active systems
- Mediterranean (2023–24)
- No active systems
- South-West Indian Ocean (2023–24)
- No active systems
- Australian region (2023–24)
- No active systems
- South Pacific (2023–24)
- No active systems
- South Atlantic (2023–24)
- No active systems
Last updated: 21:50, 2 June 2024 (UTC)
Tropical cyclone anniversaries

June 18,
- 1965 - Typhoon Dinah made landfall in Taiwan with winds of 220 km/h (140 mph). Dinah killed a total of 45 people and destroyed 5,000 homes.
- 1982 - The 1982 Florida subtropical storm (track pictured) affects Florida. Damages were recorded at $10 million.
- 2003 - Tropical Storm Blanca reaches maximum intensity with winds of 95 km/h (60 mph) and a minimum pressure of 997 hPa.

June 19,
- 1959 - Hurricane Three, which caused the 1959 Escuminac disaster, looped in the Gulf of Saint Lawrence, sinking 22 of 54 fishing boats from Escuminac, New Brunswick. The storm killed a total of 35 people.
- 1993 - Tropical Storm Arlene (pictured) reaches tropical storm intensity prior to making landfall on Padre Island, Texas. Arlene killed a total of 29 people and caused about $55 million of damage, with most of the deaths occurring while it was a tropical wave.

June 20,
- 2009 - Tropical Storm Linfa reaches peak intensity as a severe tropical storm. Linfa caused damages of about $105 million, mostly from eastern China and Taiwan.
- 2013 - Tropical Storm Barry (pictured) makes landfall over in Veracruz, Mexico, killing only five people in total.
Did you know…




- …that the Joint Typhoon Warning Center considers that Typhoon Vera (pictured) of 1986 is actually two distinct systems, formed from two separated low-level circulations?
- …that Hurricane Agatha (pictured) was the strongest Pacific hurricane to make landfall in Mexico in May since records began in 1949?
- …that Cyclone Raquel (track pictured) travelled between the Australian and South Pacific basins between the 2014–15 and 2015–16 seasons, spanning both seasons in both basins?
- …that Cyclone Amphan (pictured) in 2020 was the first storm to be classified as a Super Cyclonic Storm in the Bay of Bengal since 1999?
General images -
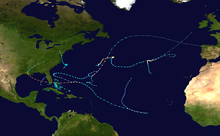
The 1992 Atlantic hurricane season was among the least active of any Atlantic hurricane season on record. It produced six named tropical cyclones. The season officially started on June 1, 1992, and ended on November 30. These dates, adopted by convention, historically delimit the period each year when most Atlantic tropical systems form. However, storm formation is possible at any time of the year, as was the case this season, when Subtropical Storm One formed on April 21. This timeline documents all the storm formations, strengthening, weakening, landfalls, extratropical transitions, as well as dissipations during the season.
During the year, three tropical depressions, one subtropical storm, two tropical storms, and four hurricanes formed. It produced seven storms, less than the average of ten usually formed throughout an Atlantic hurricane season, while four of the storms went on to become hurricanes. The first cyclone to form inside the official season was Tropical Depression One, which formed on June 25. Of the four hurricanes, Hurricane Andrew was the most intense, reaching Category 5 status. In late June, Tropical Depression One caused severe flooding in southwestern Florida and Cuba; heavy rainfall was recorded in Pinar del Río, Matanzas, and Havana. When Andrew struck Florida and Louisiana in August, it became the second-costliest hurricane to hit the United States. Damages were estimated to be about $26.5 billion and 68 people were killed. Tropical Storm Danielle made landfall at the Delmarva Peninsula on the Virginian coast on September 25, causing minimal flooding. There was one recorded death recorded due to Danielle; a ship east of New Jersey was sunk due to rough seas. The season finished on October 30 when Hurricane Frances became an extratropical gale before dissipating. (Full article...)Topics
Subcategories
Related WikiProjects
WikiProject Tropical cyclones is the central point of coordination for Wikipedia's coverage of tropical cyclones. Feel free to help!
WikiProject Weather is the main center point of coordination for Wikipedia's coverage of meteorology in general, and the parent project of WikiProject Tropical cyclones. Three other branches of WikiProject Weather in particular share significant overlaps with WikiProject Tropical cyclones:
- The Non-tropical storms task force coordinates most of Wikipedia's coverage on extratropical cyclones, which tropical cyclones often transition into near the end of their lifespan.
- The Floods task force takes on the scope of flooding events all over the world, with rainfall from tropical cyclones a significant factor in many of them.
- WikiProject Severe weather documents the effects of extreme weather such as tornadoes, which landfalling tropical cyclones can produce.
Things you can do
 |
Here are some tasks awaiting attention:
|
Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search






















































