Back بوابة:علم الفيروسات Arabic درگاه:ویروس Persian Portail:Virologie French Portal:Virus ID Portal:Vírus Portuguese ද්වාරය:වෛරස Singhalese باب:وائرسز Urdu Portal:病毒 Chinese
The Viruses Portal
Welcome!
Viruses are small infectious agents that can replicate only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all forms of life, including animals, plants, fungi, bacteria and archaea. They are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most abundant type of biological entity, with millions of different types, although only about 6,000 viruses have been described in detail. Some viruses cause disease in humans, and others are responsible for economically important diseases of livestock and crops.
Virus particles (known as virions) consist of genetic material, which can be either DNA or RNA, wrapped in a protein coat called the capsid; some viruses also have an outer lipid envelope. The capsid can take simple helical or icosahedral forms, or more complex structures. The average virus is about 1/100 the size of the average bacterium, and most are too small to be seen directly with an optical microscope.
The origins of viruses are unclear: some may have evolved from plasmids, others from bacteria. Viruses are sometimes considered to be a life form, because they carry genetic material, reproduce and evolve through natural selection. However they lack key characteristics (such as cell structure) that are generally considered necessary to count as life. Because they possess some but not all such qualities, viruses have been described as "organisms at the edge of life".
Selected disease

Hepatitis B is an infectious inflammatory disease of the liver caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV), a hepadnavirus. It affects humans and possibly other great apes. The virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or some body fluids. Mother-to-child transmission is a major route in endemic countries. HBV is 50–100 times more infectious than HIV. The virus replicates in liver cells, and enters the blood where viral proteins and antiviral antibodies are found.
Acute infection is often asymptomatic but can cause liver inflammation resulting in vomiting, jaundice and, rarely, death. Over 95% of infected adults and older children clear the infection spontaneously, developing protective immunity. Only 30% of children aged 1–6 years and 5% of newborns infected perinatally clear the infection. Chronic hepatitis B may eventually progress to cirrhosis and liver cancer, causing death in around 40% of those chronically infected. The virus has infected humans since at least the Bronze Age, with HBV DNA being found in 4,500-year-old human remains. About a third of the global population has been infected at one point in their lives, including nearly 350 million who are chronic carriers. The virus is endemic in East Asia and sub-Saharan Africa. Infection can be prevented by vaccination.
Selected image
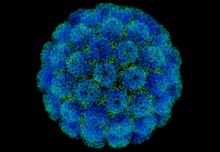
Megavirus chilensis is a very large DNA virus discovered in 2010. Until the discovery of Pandoravirus in 2013, it was the largest known virus, with its 440 nm diameter capsid being as large as some small bacteria. The capsid is enclosed in bacterial-like capsular material 75–100 nm thick.
Credit: Chantal Abergel (10 October 2011)
In the news
26 February: In the ongoing pandemic of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), more than 110 million confirmed cases, including 2.5 million deaths, have been documented globally since the outbreak began in December 2019. WHO
18 February: Seven asymptomatic cases of avian influenza A subtype H5N8, the first documented H5N8 cases in humans, are reported in Astrakhan Oblast, Russia, after more than 100,0000 hens died on a poultry farm in December. WHO
14 February: Seven cases of Ebola virus disease are reported in Gouécké, south-east Guinea. WHO
7 February: A case of Ebola virus disease is detected in North Kivu Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. WHO
4 February: An outbreak of Rift Valley fever is ongoing in Kenya, with 32 human cases, including 11 deaths, since the outbreak started in November. WHO
21 November: The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) gives emergency-use authorisation to casirivimab/imdevimab, a combination monoclonal antibody (mAb) therapy for non-hospitalised people twelve years and over with mild-to-moderate COVID-19, after granting emergency-use authorisation to the single mAb bamlanivimab earlier in the month. FDA 1, 2
18 November: The outbreak of Ebola virus disease in Équateur Province, Democratic Republic of the Congo, which started in June, has been declared over; a total of 130 cases were recorded, with 55 deaths. UN
Selected article
Viruses and viral infections have affected human history. Epidemics caused by viruses began when human behaviour changed during the Neolithic period, around 12,000 years ago. Previously hunter-gatherers, humans developed more densely populated agricultural communities, which allowed viruses to spread rapidly and subsequently to become endemic. Viruses of plants and livestock also increased, and as humans became dependent on agriculture and farming, diseases such as potyviruses of potatoes and rinderpest of cattle had devastating consequences. Smallpox and measles viruses are among the oldest that infect humans. They first appeared in humans in Europe and North Africa thousands of years ago, having evolved from viruses that infected other animals. Influenza pandemics have been recorded since 1580.
There are an estimated 1031 viruses on Earth. Although scientific interest in them arose because of the diseases they cause, most viruses are beneficial. They drive evolution by transferring genes across species, play important roles in ecosystems, and are essential to life.
Selected outbreak
The 2001 foot-and-mouth outbreak included 2,000 cases of the disease in cattle and sheep across the UK. The source was a Northumberland farm where pigs had been fed infected meat that had not been adequately sterilised. The initial cases were reported in February. The disease was concentrated in western and northern England, southern Scotland and Wales, with Cumbria being the worst-affected area. A small outbreak occurred in the Netherlands, and there were a few cases elsewhere in Europe.
The UK outbreak was controlled by the beginning of October. Control measures included stopping livestock movement and slaughtering over 6 million cows and sheep. Public access to farmland and moorland was also restricted (pictured), greatly reducing tourism in affected areas, particularly in the Lake District. Vaccination was used in the Netherlands, but not in the UK due to concerns that vaccinated livestock could not be exported. The outbreak cost an estimated £8 billion in the UK.
Selected quotation
| “ | ...classical approaches to classification are not suitable for viruses, as rigid hierarchies cannot be imposed on organisms that appear – evolutionarily speaking – to have been rather promiscuous in sharing their characteristics around. | ” |
—Ed Rybicki
Recommended articles
Viruses & Subviral agents: bat virome • elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus • HIV • introduction to viruses![]() • Playa de Oro virus • poliovirus • prion • rotavirus
• Playa de Oro virus • poliovirus • prion • rotavirus![]() • virus
• virus![]()
Diseases: colony collapse disorder • common cold • croup • dengue fever![]() • gastroenteritis • Guillain–Barré syndrome • hepatitis B • hepatitis C • hepatitis E • herpes simplex • HIV/AIDS • influenza
• gastroenteritis • Guillain–Barré syndrome • hepatitis B • hepatitis C • hepatitis E • herpes simplex • HIV/AIDS • influenza![]() • meningitis
• meningitis![]() • myxomatosis • polio
• myxomatosis • polio![]() • pneumonia • shingles • smallpox
• pneumonia • shingles • smallpox
Epidemiology & Interventions: 2007 Bernard Matthews H5N1 outbreak • Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations • Disease X • 2009 flu pandemic • HIV/AIDS in Malawi • polio vaccine • Spanish flu • West African Ebola virus epidemic
Virus–Host interactions: antibody • host • immune system![]() • parasitism • RNA interference
• parasitism • RNA interference![]()
Methodology: metagenomics
Social & Media: And the Band Played On • Contagion • "Flu Season" • Frank's Cock![]() • Race Against Time: Searching for Hope in AIDS-Ravaged Africa
• Race Against Time: Searching for Hope in AIDS-Ravaged Africa![]() • social history of viruses
• social history of viruses![]() • "Steve Burdick" • "The Time Is Now" • "What Lies Below"
• "Steve Burdick" • "The Time Is Now" • "What Lies Below"
People: Brownie Mary • Macfarlane Burnet![]() • Bobbi Campbell • Aniru Conteh • people with hepatitis C
• Bobbi Campbell • Aniru Conteh • people with hepatitis C![]() • HIV-positive people
• HIV-positive people![]() • Bette Korber • Henrietta Lacks • Linda Laubenstein • Barbara McClintock
• Bette Korber • Henrietta Lacks • Linda Laubenstein • Barbara McClintock![]() • poliomyelitis survivors
• poliomyelitis survivors![]() • Joseph Sonnabend • Eli Todd • Ryan White
• Joseph Sonnabend • Eli Todd • Ryan White![]()
Selected virus
Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) (also human herpesvirus 4) is a DNA virus in the Herpesviridae family which infects humans. The virion is around 122–180 nm in diameter. As in all herpesviruses, the nucleocapsid is surrounded by a protein tegument, as well as an envelope. The double-stranded DNA genome is about 172 kb, with 85 genes, making it one of the more complex viruses.
Transmission is via saliva and genital secretions. The virus infects epithelial cells in the pharynx and B cells of the immune system, producing virions by budding. EBV also becomes latent in B cells, possibly in the bone marrow, allowing the infection to persist lifelong. In the latent state, the linear genome is made circular and replicates in the nucleus separately from the host DNA as an episome. Reactivation is poorly understood but is thought to be triggered by the B cell responding to other infections. EBV infection occurs in around 95% of people. Infectious mononucleosis or glandular fever can occur when first infection is delayed until adolescence or adulthood. EBV is associated with some types of cancer, including Burkitt's lymphoma and nasopharyngeal carcinoma. In people with HIV, it can cause hairy leukoplakia and central nervous system lymphomas.
Did you know?
- ...that agnoprotein (pictured) is found in two polyomaviruses that can cause human disease, JC virus and BK virus?
- ...that the immunology professor Mary Collins studies ways to use genetically engineered HIV as a vaccine?
- ...that the Alternanthera mosaic virus, a type of Potexvirus, has been misdiagnosed as the closely related Papaya mosaic virus?
- ...that though once thought to be sterile, the uterine microbiome contains at least 14 commensal microorganisms in healthy women?
- ...that a form of encephalitis that killed three people is believed to have been caused by a virus carried by their pet variegated squirrels?
Selected biography
Walter Reed (13 September 1851 – 22 November 1902) was an American physician in the U.S. Army medical corps who is known for his research on the epidemiology of yellow fever, at a time when viruses had only just been discovered.
Reed started to study yellow fever in the USA in the 1890s, showing that walking through swampy woods at night was associated with the disease, while drinking water from the Potomac River was not. In 1900, he led an army commission under the direction of George Miller Sternberg to investigate yellow fever in Cuba, where the disease was endemic. Building on Carlos Finlay's work suggesting that yellow fever was transmitted by a particular species of mosquito acting as a vector, Reed and co-workers confirmed Finlay's results, and also disproved the popular idea that the disease was transmitted by contaminated objects, such as clothing or bedding. The experiments involved the deliberate infection of human volunteers, several of whom died of yellow fever, and Reed pioneered the concept of medical consent.
In this month
1 August 1971: The term viroid was coined by Theodor Diener to describe the agent of potato spindle tuber disease
6 August 2007: Maraviroc, first CCR5 receptor antagonist, approved for HIV/AIDS
8 August 2011: UN declared rinderpest eradicated
8 August 2014: WHO declared the Ebola outbreak in West Africa (virus pictured), the most widespread so far, an international public health emergency
18 August 1990: Ryan White Care Act enacted, the largest American federally funded programme for people living with HIV/AIDS
20 August 1780: Start of an outbreak of dengue fever in Philadelphia, USA, which led Benjamin Rush to describe the disease in 1789
26 August 1976: First case of Ebola virus, now the Zaire form
26 August 1998: Fomivirsen, first antisense drug, approved for cytomegalovirus retinitis
Selected intervention
Two polio vaccines are used against the paralytic disease polio. The first, developed by Jonas Salk, consists of inactivated poliovirus. Based on three wild virulent strains, inactivated using formalin, it is administered by injection and is very safe. It confers IgG-mediated immunity, which prevents poliovirus from entering the bloodstream and protects the motor neurons, eliminating the risk of bulbar polio and post-polio syndrome. The second, developed by Albert Sabin, originally consisted of three live virus strains, attenuated by growth in cell culture. Since 2016, only two strains have generally been included. They contain multiple mutations, preventing them from replicating in the nervous system. The Sabin vaccine stimulates both antibodies and cell-mediated immunity, providing longer-lasting immunity than the Salk vaccine. It can be administered orally, making it more suitable for mass vaccination campaigns. In around three cases per million doses, the live vaccine reverts to a virulent form and causes paralysis. Vaccination has reduced the number of wild-type polio cases from around 350,000 in 1988 to just 33 in 2018, and eradicated the disease from most countries.
Subcategories
Subcategories of virology:
Topics
Things to do
- Comment on what you like and dislike about this portal
- Join the Viruses WikiProject
- Tag articles on viruses and virology with the project banner by adding {{WikiProject Viruses}} to the talk page
- Assess unassessed articles against the project standards
- Create requested pages: red-linked viruses | red-linked virus genera
- Expand a virus stub into a full article, adding images, citations, references and taxoboxes, following the project guidelines
- Create a new article (or expand an old one 5-fold) and nominate it for the main page Did You Know? section
- Improve a B-class article and nominate it for Good Article
 or Featured Article
or Featured Article status
status - Suggest articles, pictures, interesting facts, events and news to be featured here on the portal
WikiProjects & Portals
 WikiProject Viruses
Related WikiProjects
WikiProject Viruses
Related WikiProjects
Medicine • Microbiology • Molecular & Cellular Biology • Veterinary Medicine
Related PortalsAssociated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search