
Back Руги Bulgarian Rugis Catalan Rugiové Czech Ругсем CV Rugiere Danish Rugier German Rugoj Esperanto Rugios Spanish Ruugit Finnish Ruges French
The Rugii, Rogi or Rugians (Ancient Greek: Ρογοί, romanized: Rogoi), were one of the smaller Germanic peoples of Late Antiquity who are best known for their short-lived 5th-century kingdom upon the Roman frontier, near present-day Krems an der Donau in Austria.[1] This kingdom, like those of the neighbouring Heruli and Scirii, first appeared after the death of Attila in 453. The Rugii, Heruli, Scirii and others are believed to have moved into this region from distant homelands under pressure from the Huns, and then become part of Attila's empire when it also came to be based in this region. The Rugii were also part of the alliance who defeated Attila's sons and the Ostrogoths at the Battle of Nedao in 454, giving their kingdom independence. In 469 they were part of a similar alliance who lost to the Ostrogoths at the Battle of Bolia, weakening their kingdom significantly.
Many Rugii, once again along with Scirii, Heruli and other Danubians, joined Odoacer in Italy and became part of his kingdom there. Fearing new plots against him, he invaded the Rugian kingdom in 487, and the Rugian lands were then settled by the Lombards from the north. Most Rugii still in the Danubian region eventually joined the Ostrogoth Theoderic the Great who killed Odoacer and established a Gothic-led regime in Italy, in which the Rugii played a role until it was destroyed by Justinian. The third last king of this Ostrogothic kingdom was the Rugian Eraric who died in 541. After him the Rugians disappear from history.
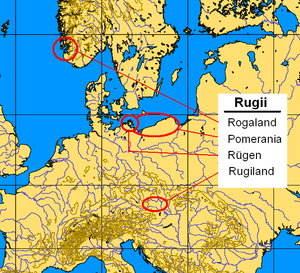
It is generally accepted that the Rugii were first clearly recorded by Tacitus in the first century, in his Germania. He mentioned a people called the Rugii living near the south shore of the Baltic Sea, near the Lemovii and east of the Gutones who apparently lived near the mouth of the Vistula. The 6th century writer Procopius included them among the "Gothic peoples", grouping them with Goths, Gepids, Vandals, Sciri, and the non-Germanic Alans, who were mainly associated with Eastern Europe.[2]
Various other records mentioning places or peoples with similar names have been associated with the Danubian Rugii. Another 6th century writer, Jordanes says there were "Rugi" living in Scandinavia in his own time, near the Dani (Danes) and Suetidi (Suedes), although he does not explain if they are related to the Rugii who had been living near the Danube. The medieval Rygir were a tribe residing in Rogaland of southwestern Norway, around the Boknafjord. The Baltic Rugii mentioned by Tacitus are also possibly related to the Rutikleioi, and the place known as Rougion, both mentioned on the southern Baltic coast in the second century by Ptolemy. The coastal island known today as Rügen is also sometimes associated with the Rugii. The Rugii are also associated with the Ulmerugi, whose name probably means "island Rugii", who are mentioned in the sixth century by Jordanes as a people who had lived on the Baltic coast near the Vistula, many centuries earlier when, according to him, the Goths arrived by boat from Scandinavia. A similar island name Holmrygir is known from much later medieval Norway, in the area near Rogaland.
The name of the Rugii continued to be used after the sixth century to refer to Slavic-speaking peoples including even Russians.[3]
- ^ Bjornlie, Shane (2018). "Rugians". In Nicholson, Oliver (ed.). The Oxford Dictionary of Late Antiquity. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780191744457. Retrieved January 26, 2020.
Rugians. Germanic people prominent in provincial politics of the Danube frontier region during the last half of the 5th century...
- ^ See for example Wolfram (2005, p. 77) and Steinacher (2017, p. 28).
- ^ Steinacher, Roland [in German] (2010). "The Herules: Fragments of a History". In Curta, Florin (ed.). Neglected Barbarians. ISD. ISBN 9782503531250. pp.43-44.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search