
Back SOFA-Score German SOFA Spanish SOFA-järjestelmä Finnish Score SOFA French Nilai SOFA ID SOFA-score Dutch Skala SOFA Polish คะแนนโซฟา Thai
| SOFA score | |
|---|---|
 A patient's SOFA score assessment | |
| Purpose | determine rate of organ failure |
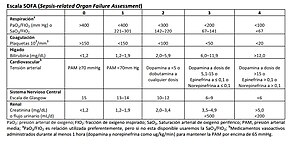
The sequential organ failure assessment score (SOFA score), previously known as the sepsis-related organ failure assessment score,[1] is used to track a person's status during the stay in an intensive care unit (ICU) to determine the extent of a person's organ function or rate of failure.[2][3][4][5][6] The score is based on six different scores, one each for the respiratory, cardiovascular, hepatic, coagulation, renal and neurological systems.
The score tables below only describe points-giving conditions. In cases where the physiological parameters do not match any row, zero points are given. In cases where the physiological parameters match more than one row, the row with most points is picked.
The quick SOFA score (qSOFA) assists health care providers in estimating the risk of morbidity and mortality due to sepsis.[7]
- ^ Singer, Mervyn; et al. (23 February 2016). "The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3)". JAMA. 315 (8): 801–10. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.0287. PMC 4968574. PMID 26903338.
- ^ Vincent JL, Moreno R, Takala J, Willatts S, De Mendonça A, Bruining H, Reinhart CK, Suter PM, Thijs LG (Jul 1996). "The SOFA (Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure. On behalf of the Working Group on Sepsis-Related Problems of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine". Intensive Care Med. 22 (7): 707–10. doi:10.1007/bf01709751. PMID 8844239. S2CID 40396839.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Vincent JL, de Mendonça A, Cantraine F, Moreno R, Takala J, Suter PM, Sprung CL, Colardyn F, Blecher S (Nov 1998). "Use of the SOFA score to assess the incidence of organ dysfunction/failure in intensive care units: results of a multicenter, prospective study. Working group on "sepsis-related problems" of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine". Crit Care Med. 26 (11): 1793–800. doi:10.1097/00003246-199811000-00016. PMID 9824069. S2CID 28070236.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Moreno R, Vincent JL, Matos R, Mendonça A, Cantraine F, Thijs L, Takala J, Sprung C, Antonelli M, Bruining H, Willatts S (Jul 1999). "The use of maximum SOFA score to quantify organ dysfunction/failure in intensive care. Results of a prospective, multicentre study. Working Group on Sepsis related Problems of the ESICM". Intensive Care Med. 25 (7): 686–96. doi:10.1007/s001340050931. PMID 10470572. S2CID 34510892.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ de Mendonça A, Vincent JL, Suter PM, Moreno R, Dearden NM, Antonelli M, Takala J, Sprung C, Cantraine F (Jul 2000). "Acute renal failure in the ICU: risk factors and outcome evaluated by the SOFA score". Intensive Care Med. 26 (7): 915–21. doi:10.1007/s001340051281. PMID 10990106. S2CID 24304874.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Ferreira FL, Bota DP, Bross A, Mélot C, Vincent JL (Oct 2001). "Serial evaluation of the SOFA score to predict outcome in critically ill patients". JAMA. 286 (14): 1754–8. doi:10.1001/jama.286.14.1754. PMID 11594901.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "National Inpatient Hospital Costs: The Most Expensive Conditions by Payer, 2013". www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Retrieved 2017-01-07.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search