
Back استعمار استيطاني Arabic Məskunlaşma kolonializmi Azerbaijani Siedlungskolonie German Colonialismo de poblamiento Spanish استعمار مهاجرنشین Persian Asuttajakolonialismi Finnish Colonie de peuplement French Turawan mulkin mallaka Hausa קולוניאליזם התיישבותי HE Kolonialisme pemukim ID
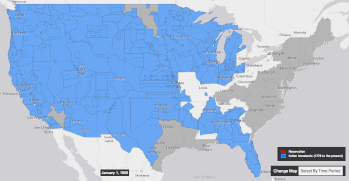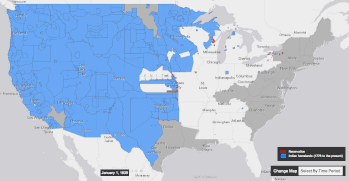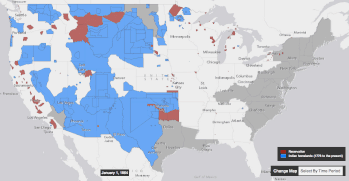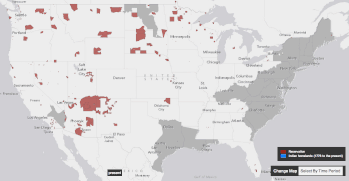
Settler colonialism occurs when colonizers and settlers invade and occupy territory to permanently replace the existing society with the society of the colonizers.[1][2][3]
Settler colonialism is a form of exogenous domination[clarification needed] typically organized or supported by an imperial authority, which maintains a connection or control to the territory through the settler's colonialism.[4] Settler colonialism contrasts with exploitation colonialism, where the imperial power conquers territory to exploit the natural resources and gain a source of cheap or free labor. As settler colonialism entails the creation of a new society on the conquered territory, it lasts indefinitely unless decolonisation occurs through removal of the settler population or (more debatably) through reforms to colonial structures, settler-indigenous compacts and reconciliation processes.[a][5]
Settler colonial studies has often focused on former British colonies in North America, Australia and New Zealand, which are close to the complete, prototypical form of settler colonialism.[6] However, settler colonialism is not restricted to any specific culture and has been practised by non-Europeans.[2]
- ^ Carey, Jane; Silverstein, Ben (2 January 2020). "Thinking with and beyond settler colonial studies: new histories after the postcolonial". Postcolonial Studies. 23 (1): 1–20. doi:10.1080/13688790.2020.1719569. hdl:1885/204080. S2CID 214046615.
The key phrases Wolfe coined here – that invasion is a 'structure not an event'; that settler colonial structures have a 'logic of elimination' of Indigenous peoples; that 'settlers come to stay' and that they 'destroy to replace' – have been taken up as the defining precepts of the field and are now cited by countless scholars across numerous disciplines.
- ^ a b Veracini, Lorenzo (2017). "Introduction: Settler colonialism as a distinct mode of domination". In Cavanagh, Edward; Veracini, Lorenzo (eds.). The Routledge Handbook of the History of Settler Colonialism. Routledge. p. 4. ISBN 978-0-415-74216-0.
Settler colonialism is a relationship. It is related to colonialism but also inherently distinct from it. As a system defined by unequal relationships (like colonialism) where an exogenous collective aims to locally and permanently replace indigenous ones (unlike colonialism), settler colonialism has no geographical, cultural or chronological bounds. It is culturally nonspecific ... It can happen at any time, and everyone is a settler if they are part of a collective and sovereign displacement that moves to stay, that moves to establish a permanent homeland by way of displacement.
- ^ McKay, Dwanna L.; Vinyeta, Kirsten; Norgaard, Kari Marie (September 2020). "Theorizing race and settler colonialism within U.S. sociology". Sociology Compass. 14 (9). doi:10.1111/soc4.12821. ISSN 1751-9020. S2CID 225377069.
Settler-colonialism describes the logic and operation of power when colonizers arrive and settle on lands already inhabited by another group. Importantly, settler colonialism operates through a logic of elimination, seeking to eradicate the original inhabitants through violence and other genocidal acts and to replace the existing spiritual, epistemological, political, social, and ecological systems with those of the settler society.
- ^ LeFevre, Tate. "Settler Colonialism". oxfordbibliographies.com. Tate A. LeFevre. Retrieved 19 October 2017.
Though often conflated with colonialism more generally, settler colonialism is a distinct imperial formation. Both colonialism and settler colonialism are premised on exogenous domination, but only settler colonialism seeks to replace the original population of the colonized territory with a new society of settlers (usually from the colonial metropole).
- ^ Veracini, Lorenzo (October 2007). "Settler Colonialism and Decolonisation". Borderlands. 6 (2).
- ^ Englert, Sai (2020). "Settlers, Workers, and the Logic of Accumulation by Dispossession". Antipode. 52 (6): 1647–1666. Bibcode:2020Antip..52.1647E. doi:10.1111/anti.12659. hdl:1887/3220822. S2CID 225643194.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search