
Back بنية تحتية حضرية مستدامة Arabic Infraestructura urbana sostenible Spanish Ihe owuwu obodo na-adịgide adịgide IG اوږدپایه ښاري بېخبنا Pashto/Pushto
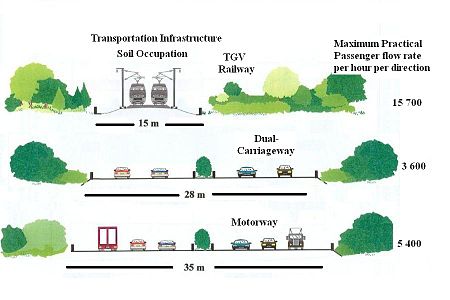
Sustainable urban infrastructure expands on the concept of urban infrastructure by adding the sustainability element with the expectation of improved and more resilient urban development. In the construction and physical and organizational structures that enable cities to function, sustainability also aims to meet the needs of the present generation without compromising the capabilities of the future generations.[1]
SDG 9, of the international Sustainable Development Goals set by the United Nations General Assembly, deals with infrastructure, however, infrastructure is a building block for the rest of the SDGs. Therefore, the achievement of sustainable infrastructure is of significant concern in multiple areas of society.[2]
The sustainable development of urban areas is crucial since more than 56% of the world's population lives in cities. Cities are in the lead of climate action, while being responsible for an estimated 75% of the world's carbon emissions. [3][4][5][6]
- ^ Tiwari, Alok (2016). Urban Infrastructure Research: A Review of Ethiopian Cities. SpringerBriefs in Geography. London: Springer. p. 2. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-30403-8. ISBN 978-3-319-30401-4. ISSN 2211-4165. S2CID 132730314.
- ^ "the critical role of infrastructure for the sdgs" (PDF).
- ^ Bank, European Investment (6 July 2022). EIB Group Sustainability Report 2021. European Investment Bank. ISBN 978-92-861-5237-5.
- ^ Environment, U. N. (26 September 2017). "Cities and climate change". UNEP - UN Environment Programme. Retrieved 27 July 2022.
- ^ "Urban Climate Action Is Crucial to Bend the Emissions Curve". United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change. 5 October 2020. Archived from the original on 5 April 2023. Retrieved 27 July 2023.
- ^ "Cities: a 'cause of and solution to' climate change". UN News. 18 September 2019. Retrieved 27 July 2022.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search