Back ثرومبين Arabic Trombin Azerbaijani Трамбін Byelorussian Трамбін BE-X-OLD Тромбин Bulgarian Trombin BS Trombina Catalan Thrombin Danish Thrombin German Trombina Spanish

Prothrombin (Coagulation factor II) is encoded in the human by the F2 gene. It is proteolytically cleaved during the clotting process by the prothrombinase enzyme complex to form thrombin.
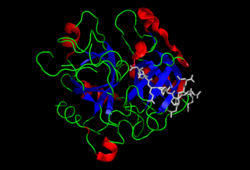
Thrombin (Factor IIa) (EC 3.4.21.5, fibrinogenase, thrombase, thrombofort, topical, thrombin-C, tropostasin, activated blood-coagulation factor II, E thrombin, beta-thrombin, gamma-thrombin) is a serine protease, that converts fibrinogen into strands of insoluble fibrin, as well as catalyzing many other coagulation-related reactions.[5][6]
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000180210 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000027249 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Royle NJ, Irwin DM, Koschinsky ML, MacGillivray RT, Hamerton JL (May 1987). "Human genes encoding prothrombin and ceruloplasmin map to 11p11-q12 and 3q21-24, respectively". Somatic Cell and Molecular Genetics. 13 (3): 285–92. doi:10.1007/BF01535211. PMID 3474786. S2CID 45686258.
- ^ Degen SJ, Davie EW (September 1987). "Nucleotide sequence of the gene for human prothrombin". Biochemistry. 26 (19): 6165–77. doi:10.1021/bi00393a033. PMID 2825773.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search