
Back إنتاجية القوى العاملة Arabic Əmək məhsuldarlığı Azerbaijani Darba našoms BAT-SMG Производителност на труда Bulgarian Produktivita práce Czech Arbeitsproduktivität German פריון העבודה HE Munkatermelékenység Hungarian Еңбек өнімділігі Kazakh 노동 생산성 Korean
| Part of a series on |
| Economics |
|---|
Workforce productivity is the amount of goods and services that a group of workers produce in a given amount of time. It is one of several types of productivity that economists measure. Workforce productivity, often referred to as labor productivity, is a measure for an organisation or company, a process, an industry, or a country.
Workforce productivity is to be distinguished from employee productivity which is a measure employed at the individual level based on the assumption that the overall productivity can be broken down into increasingly smaller units until, ultimately, to the individual employee, in order be used for example for the purpose of allocating a benefit or sanction based on individual performance (see also: Vitality curve).
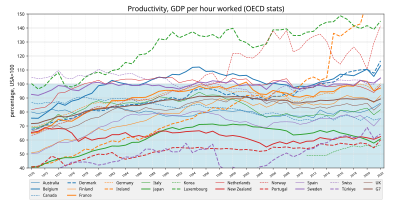
The OECD defines productivity as "a ratio between the volume of output and the volume of inputs".[1] Volume measures of output are normally gross domestic product (GDP) or gross value added (GVA), expressed at constant prices i.e. adjusted for inflation. The three most commonly used measures of input are:
- hours worked, typically from the OECD Annual National Accounts database[2]
- workforce jobs; and
- number of people in employment.
- ^ "Productivity". OECD iLibrary. Retrieved 2024-03-15.
- ^ "Defining and Measuring Productivity" (PDF). 2017-04-19. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-04-19. Retrieved 2017-10-13.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search