
Back Diabetes Afrikaans Diabetes mellitus ALS ስኳር በሽታ Amharic Diabetis mellitus AN السكري Arabic مرض السكر ARZ বহুমূত্ৰ ৰোগ Assamese Diabetes mellitus AST सुगर रोग AWA Şəkərli diabet Azerbaijani
This article has many issues. Please help fix them or discuss these issues on the article's talk page.
|
| Diabetes mellitus | |
|---|---|
| Classification and external resources | |
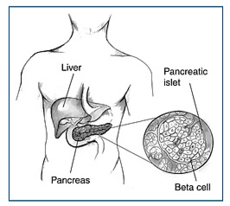 Insulin is made in beta cells in the pancreas. Problems with insulin causes diabetes. | |
| ICD-10 | E10.–E14. |
| ICD-9 | 250 |
| MedlinePlus | 001214 |
| eMedicine | med/546 emerg/134 |
| MeSH | C18.452.394.750 |
Diabetes is a condition that results from lack of the hormone insulin in a person's blood, or when the body has a problem using the insulin it produces (insulin resistance). People with diabetes Mellitus are called diabetics.
There is another disease with a similar name, diabetes insipidus, however, they are not related. When people say "diabetes", they usually mean diabetes mellitus.
Diabetes entered the top 10 causes of death in 2019, following a significant percentage increase of 70% since 2000. Diabetes is also responsible for the largest rise in male deaths among the top 10, with an 80% increase since 2000.[1]
Glucose is not regular sugar that is available in stores and supermarkets. Glucose is a natural carbohydrate that our bodies use as a source of energy. The kind of sugar sold in supermarkets is called sucrose, and is much different from glucose. High concentrations of glucose can be found in soft drinks and fruits.[2]
The glucose level in the blood is controlled by several hormones. Hormones are chemicals in the body that send messages from cells to other cells. Insulin is a hormone made by the pancreas. When you eat, the pancreas makes insulin to send a message to other cells in the body. This insulin tells the cells to take up glucose from the blood. The glucose is used by cells for energy. Extra glucose that is not needed right away is stored in some cells as glycogen. When you are not eating, cells break down the stored glycogen into glucose to use as energy.
- ↑ "The top 10 causes of death". www.who.int. Retrieved 2024-05-22.
- ↑ "What is glucose? What does "bG" mean?" (HTML). FAQS.ORG. Retrieved 2009-02-10.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search