
Back توسع الناتو Arabic Proširenje NATO-a BS فراوانبوونی ناتۆ CKB Ehangu NATO Welsh NATO-Erweiterung German Διεύρυνση του ΝΑΤΟ Greek Ampliación de la OTAN Spanish NATOren zabalpena Basque گسترش ناتو Persian Élargissement de l'OTAN French
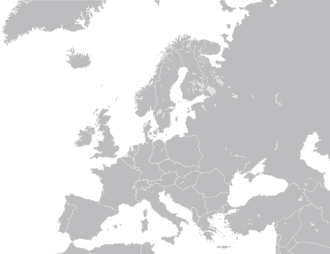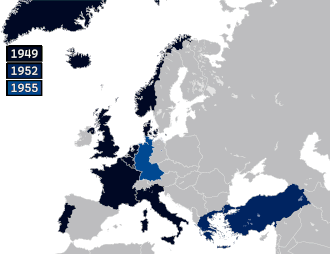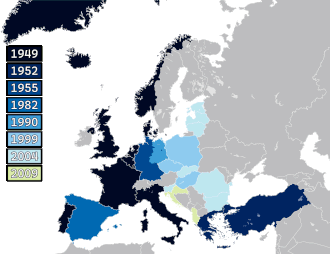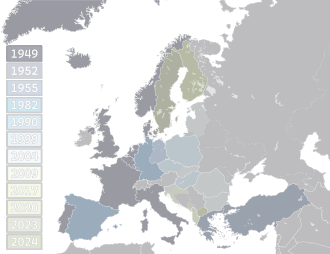
NATO is a military alliance of thirty-two European and North American countries that constitutes a system of collective defense. The process of joining the alliance is governed by Article 10 of the North Atlantic Treaty, which allows for the invitation of "other European States" only and by subsequent agreements. Countries wishing to join must meet certain requirements and complete a multi-step process involving political dialog and military integration. The accession process is overseen by the North Atlantic Council, NATO's governing body. NATO was formed in 1949 with twelve founding members and has added new members ten times. The first additions were Greece and Turkey in 1952. In May 1955, West Germany joined NATO, which was one of the conditions agreed to as part of the end of the country's occupation by France, the United Kingdom, and the United States, prompting the Soviet Union to form its own collective security alliance (commonly called the Warsaw Pact) later that month. Following the end of the Franco regime, newly democratic Spain chose to join NATO in 1982.
In 1990, the negotiators reached an agreement that a reunified Germany would be in NATO under West Germany's existing membership. Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, many former Warsaw Pact and post-Soviet states sought to join NATO. Poland, Hungary, and the Czech Republic became NATO members in 1999, amid much debate within NATO itself and Russian opposition. NATO then formalized the process of joining the organization with "Membership Action Plans", which aided the accession of seven Central and Eastern Europe countries shortly before the 2004 Istanbul summit: Bulgaria, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Romania, Slovakia, and Slovenia. Two countries on the Adriatic Sea—Albania and Croatia—joined on 1 April 2009 before the 2009 Strasbourg–Kehl summit. The next member states to join NATO were Montenegro on 5 June 2017, and North Macedonia on 27 March 2020.
Russia invaded Ukraine in 2022 after Russia's president, Vladimir Putin, falsely claimed that NATO military infrastructure was being built up inside Ukraine and that Ukraine's potential future membership was a threat. Russia's invasion prompted Finland and Sweden to apply for NATO membership in May 2022.[1] Finland joined on 4 April 2023, and Sweden joined on 7 March 2024.[2][3][4] Ukraine applied for NATO membership in September 2022 after Russia proclaimed the annexation of its territory.[1] Two other states have formally informed NATO of their membership aspirations: Bosnia and Herzegovina and Georgia.[5] Kosovo also aspires to join NATO.[6] Joining the alliance is a debate topic in several other European countries outside the alliance, including Austria, Cyprus, Ireland, Malta, Moldova, and Serbia.[7]
- ^ a b Harding, Luke; Koshiw, Isobel (30 September 2022). "Ukraine applies for Nato membership after Russia annexes territory". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 1 October 2022. Retrieved 30 September 2022.
- ^ Jackson, John (29 June 2022). "Ukraine Sees Opportunity to Join NATO After Finland, Sweden Invite". Newsweek. Archived from the original on 30 June 2022. Retrieved 30 June 2022.
- ^ "NATO launches ratification process for Sweden, Finland membership". France24. 5 July 2022. Archived from the original on 5 July 2022. Retrieved 5 July 2022.
- ^ "NATO - Sweden Accession Protocol - Notification of Entry Into Force, March 7, 2024". United States Department of State. 7 March 2024. Retrieved 7 March 2024.
- ^ "Enlargement". The North Atlantic Treaty Organization. 5 May 2020. Archived from the original on 9 June 2021. Retrieved 11 June 2021.
- ^ "Kosovo asks U.S. for permanent military base, speedier NATO membership". Reuters. 27 February 2022. Archived from the original on 27 February 2022. Retrieved 27 February 2022.
- ^ Fehlinger, Gunther (9 October 2022). "Malta, Austria and Ireland united in NATO 2023 – Gunther Fehlinger". Times of Malta. Archived from the original on 3 November 2022. Retrieved 3 November 2022.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search