
Back ۲۵آی-انبام AZB 25I-NBOMe German 25I-NBOMe Spanish ۲۵آی-انبام Persian 25I-NBOMe Finnish 25I-NBOMe French 25I-NBOMe Hungarian 25I-NBOMe Italian 25I-NBOMe Latvian/Lettish 25I-NBOMe Portuguese
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 2C-I-NBOMe; 25I; 25i; N-Bomb; Smiles; Wizard; INBMeO; Cimbi-5; Cimbi-5-2; N-(2-Methoxybenzyl)-4-iodo-2,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine; 4-Iodo-2,5-dimethoxy-N-(2-methoxybenzyl)phenethylamine |
| Routes of administration | Mainly sublingual, buccal, and insufflation[1] |
| Drug class | Serotonin 5-HT2 receptor agonist; Serotonergic psychedelic; Hallucinogen[1] |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Very low[1] |
| Metabolism | Extensive first-pass metabolism in the liver[1] |
| Onset of action | 15–120 min (0.25–2 hours)[1] |
| Duration of action | Insufflation: 4–6 h[1] Sublingual: 6–10 h[1] Buccal: 6–10 h[1] |
| Excretion | Urine[1] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
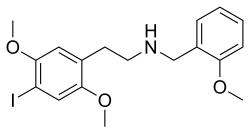
| Formula | C18H22INO3 |
| Molar mass | 427.282 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
25I-NBOMe, also known as 2C-I-NBOMe, Cimbi-5, and shortened to "25I", is a psychedelic drug of the phenethylamine, 2C, and NBOMe (25-NB) families.[1] Since 2010, it has circulated in the recreational drug scene, often misrepresented as LSD.[6] It is the most well-known member of the 25-NB family and the earliest member to be encountered as a novel recreational drug.[6]
The drug was first described in the scientific literature by Ralf Heim and colleagues at the Free University of Berlin by 2000.[7][8][9] Other NBOMe derivatives such as 25B-NBOMe and 2CBFly-NBOMe were also described in the same publications.[7][8] 25I-NBOMe was subsequently further investigated by a team at Purdue University led by David Nichols.[10][11][12]
The carbon-11 labelled version of 25I-NBOMe, [11C]Cimbi-5, was synthesized and validated as a radiotracer for positron emission tomography (PET) in Copenhagen.[13][14] Being the first 5-HT2A receptor full agonist PET radioligand, [11C]CIMBI-5 shows promise as a more functional marker of these receptors, particularly in their high affinity states.[13]
Street and media nicknames for this drug include "N-Bomb", "Solaris", "Smiles", and "Wizard", although the drug is frequently fraudulently sold as LSD.[1][15][16][17]
Due to its physical effects and risk of overdose, there have been multiple deaths attributed to the drug.[1] Its long-term toxicity is unknown due to lack of existing research.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Nikolaou P, Papoutsis I, Stefanidou M, Spiliopoulou C, Athanaselis S (January 2015). "2C-I-NBOMe, an "N-bomb" that kills with "Smiles". Toxicological and legislative aspects". Drug Chem Toxicol. 38 (1): 113–119. doi:10.3109/01480545.2014.911882. PMID 24785196.
- ^ Anvisa (2023-07-24). "RDC Nº 804 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 804 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Diário Oficial da União (published 2023-07-25). Archived from the original on 2023-08-27. Retrieved 2023-08-27.
- ^ "Regulations Amending the Food and Drug Regulations (Part J — 2C-phenethylamines)". Canada Gazette. 4 May 2016. Archived from the original on 2016-08-31. Retrieved 2016-08-22.
- ^ UK Home Office (2014). "The Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 (Ketamine etc.) (Amendment) Order 2014". UK Government. Archived from the original on 2014-12-04. Retrieved 2014-03-11.
- ^ "Substance Details 25I-NBOMe". Archived from the original on 2024-01-23. Retrieved 2024-01-23.
- ^ a b Herian M, Wojtas A, Kamińska K, Świt P, Wach A, Gołembiowska K (July 2019). "Hallucinogen-Like Action of the Novel Designer Drug 25I-NBOMe and Its Effect on Cortical Neurotransmitters in Rats". Neurotox Res. 36 (1): 91–100. doi:10.1007/s12640-019-00033-x. PMC 6570696. PMID 30989482.
The NBOMes became available to drug users when they first appeared on the drug market in 2010, with 25I-NBOMe emerging as the earliest (Halberstadt 2017; Poklis et al. 2015; Zuba et al. 2013).
- ^ a b Heim R, Elz S (March 2000). "39. Novel Extremely Potent Partial 5-HT2A-Receptor Agonists: Successful Application of a New Structure-Activity Concept". Arch. Pharm. Pharm. Med. Chem. 333 (Suppl 1): 1–40 (18). ISSN 0365-6233. Archived from the original on 20 March 2025.
- ^ a b Pertz HH, Heim R, Elz S (2000). "B 1.11. N-Benzylated phenylethanamines are highly potent partial agonists at 5-HT2A receptors". Arch. Pharm. Pharm. Med. Chem. 333 (Suppl 2): 1–84 (30). Archived from the original on 20 March 2025.
- ^ Heim R (25 March 2003). "Synthese und Pharmakologie potenter 5-HT2A-Rezeptoragonisten mit N-2-Methoxybenzyl-Partialstruktur. Entwicklung eines neuen Struktur-Wirkungskonzepts" [Synthesis and pharmacology of potent 5-HT2A receptor agonists with an N-2-methoxybenzyl partial structure. Development of a new structure-activity concept.] (in German). diss.fu-berlin.de. Archived from the original on 2012-04-16. Retrieved 2013-05-10.
- ^ Braden MR, Parrish JC, Naylor JC, Nichols DE (December 2006). "Molecular interaction of serotonin 5-HT2A receptor residues Phe339(6.51) and Phe340(6.52) with superpotent N-benzyl phenethylamine agonists". Mol Pharmacol. 70 (6): 1956–1964. doi:10.1124/mol.106.028720. PMID 17000863.
- ^ Braden MR (2007). "Towards a biophysical understanding of hallucinogen action". Dissertation. Purdue University: 1–176. Archived from the original on 2016-09-19. Retrieved 2016-07-19.
- ^ Nichols DE, Frescas SP, Chemel BR, Rehder KS, Zhong D, Lewin AH (June 2008). "High specific activity tritium-labeled N-(2-methoxybenzyl)-2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenethylamine (INBMeO): a high-affinity 5-HT2A receptor-selective agonist radioligand". Bioorg Med Chem. 16 (11): 6116–6123. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2008.04.050. PMC 2719953. PMID 18468904.
Recently, we reported on a series of high affinity N-benzyl phenethylamine ligands for the 5-HT2A receptor.14 The most potent of the ones reported, N-(2- methoxybenzyl)-2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenethylamine (INBMeO, 1), had exceptionally high affinity for the 5-HT2A receptor, [...] 14. Braden MR, Parrish JC, Naylor JC, Nichols DE. Mol Pharmacol 2006;70:1956–1964. [PubMed: 17000863]
- ^ a b Ettrup A, Palner M, Gillings N, Santini MA, Hansen M, Kornum BR, et al. (November 2010). "Radiosynthesis and evaluation of 11C-CIMBI-5 as a 5-HT2A receptor agonist radioligand for PET". Journal of Nuclear Medicine. 51 (11): 1763–1770. doi:10.2967/jnumed.109.074021. PMID 20956470.
- ^ Hansen M (16 December 2010). "Design and synthesis of selective serotonin receptor agonists for positron emission tomography imaging of the brain". Ph.D. Thesis. Det Farmaceutiske Fakultet, København. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.690.4529.
- ^ "Erowid 25I-NBOMe Vault". Archived from the original on 2016-06-30. Retrieved 2016-06-28.
- ^ Vanderbilt University Medical Center (9 April 2015). "Poison center warns against designer drug 'N-bomb'". ScienceDaily. Archived from the original on 9 May 2016. Retrieved 14 April 2016.
- ^ Mackin, Teresa (October 9, 2012). Dangerous synthetic drug making its way across the country. Archived October 31, 2012, at the Wayback Machine WISH-TV
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search