
Back Triple unión de Afar Spanish Jonction triple de l'Afar French Tripla giunzione di Afar Italian 아파르 삼중합점 Korean Jonccion tripla d'Afar Occitan Węzeł potrójny Afar Polish Афарський трійник Ukrainian
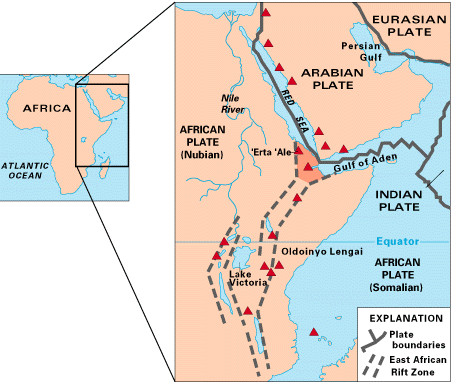
The Afar Triple Junction (also called the Afro-Arabian Rift System) is located along a divergent plate boundary dividing the Nubian, Somali, and Arabian plates. This area is considered a present-day example of continental rifting leading to seafloor spreading and producing an oceanic basin. Here, the Red Sea Rift meets the Aden Ridge and the East African Rift. The latter extends a total of 6,500 kilometers (4,000 mi) from the Afar Triangle to Mozambique.[1]
The connecting three arms form a triple junction. The northernmost branching arm extends north through the Red Sea and into the Dead Sea, while the eastern arm extends through the Gulf of Aden and connects to the Mid-Indian Ocean ridge further to the east. Both of these rifting arms are below sea level and are similar to a mid-ocean ridge.[1]
The third rifting arm runs south extending around 4,000 kilometres (2,500 mi) through the countries of Kenya, Uganda, the Democratic Republic of Congo, Rwanda, Burundi, Tanzania, Zambia, Malawi and, finally, Mozambique. This southern rifting arm is better known as the East African Rift or the East African Rift System (EARS), when it includes the Afar Triangle.
- ^ a b Chorowicz, Jean (1 October 2005). "The East African rift system". Journal of African Earth Sciences. 43 (1–3): 379–410. Bibcode:2005JAfES..43..379C. doi:10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2005.07.019.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search