Back بنكسية كوكبية Arabic بانكسيا كوكبيه ARZ Banksia verticillata Azerbaijani Banksia verticillata Esperanto Banksia verticillata Spanish بانکسیا خارا Persian Banksia verticillata French Banksia verticillata ID Banksia verticillata Italian Banksia verticillata Dutch
| Granite banksia | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Order: | Proteales |
| Family: | Proteaceae |
| Genus: | Banksia |
| Species: | B. verticillata
|
| Binomial name | |
| Banksia verticillata | |

| |
| Distribution of B. verticillata in Western Australia. | |
Banksia verticillata, commonly known as granite banksia or Albany banksia, is a species of shrub or (rarely) tree of the genus Banksia in the family Proteaceae. It is native to the southwest of Western Australia and can reach up to 3 m (10 ft) in height. It can grow taller to 5 m (16 ft) in sheltered areas, and much smaller in more exposed areas. This species has elliptic green leaves and large, bright golden yellow inflorescences or flower spikes, appearing in summer and autumn. The New Holland honeyeater (Phylidonyris novaehollandiae) is the most prominent pollinator, although several other species of honeyeater, as well as bees, visit the flower spikes.
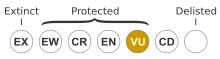
A declared vulnerable species, it occurs in two disjunct populations on granite outcrops along the south coast of Western Australia, with the main population near Albany and a smaller population near Walpole, and is threatened by dieback (Phytophthora cinnamomi) and aerial canker (Zythiostroma). B. verticillata is killed by bushfire and new plants regenerate from seed afterwards. Populations take over a decade to produce seed and fire intervals of greater than twenty years are needed to allow the canopy seed bank to accumulate.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search