
Back تشنج قصبي Arabic Bronxospazm Azerbaijani برونخوسپازم AZB Broncospasme Catalan Bronkospasme Danish Bronchospasmus German Broncoespasmo Spanish اسپاسم برونش Persian Bronchospasme French ब्रोंकोस्पजम Hindi
| Bronchospasm | |
|---|---|
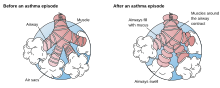 | |
| Inflamed airways and bronchoconstriction in asthma. Airways narrowed as a result of the inflammatory response cause wheezing. | |
| Specialty | Pulmonology |
Bronchospasm or a bronchial spasm is a sudden constriction of the muscles in the walls of the bronchioles. It is caused by the release (degranulation) of substances from mast cells or basophils under the influence of anaphylatoxins. It causes difficulty in breathing which ranges from mild to severe.
Bronchospasms occur in asthma, chronic bronchitis and anaphylaxis. Bronchospasms are a possible side effect of some drugs: pilocarpine, beta blockers (used to treat hypertension), a paradoxical result of using LABA drugs (to treat COPD), and other drugs. Bronchospasms can present as a sign of giardiasis.
Some factors that contribute to bronchospasm include consuming certain foods, taking certain medicines, allergic responses to insects, and fluctuating hormone levels, particularly in women.[1][2] Bronchospasms are one of several conditions associated with cold housing.[3]
The overactivity of the bronchioles' muscle is a result of exposure to a stimulus which under normal circumstances would cause little or no response. The resulting constriction and inflammation causes a narrowing of the airways and an increase in mucus production; this reduces the amount of oxygen that is available to the individual causing breathlessness, coughing and hypoxia.
Bronchospasms are a serious potential complication of placing a breathing tube during general anesthesia. When the airways spasm or constrict in response to the irritating stimulus of the breathing tube, it is difficult to maintain the airway and the patient can become apneic. During general anesthesia, signs of bronchospasm include wheezing, high peak inspiratory pressures, increased intrinsic PEEP, decreased expiratory tidal volumes, and an upsloping capnograph (obstructive pattern). In severe cases, there may be complete inability to ventilate and loss of ETCO2 as well as hypoxia and desaturation.
- ^ Haggerty, Catherine L.; Ness, Roberta B.; Kelsey, Sheryl; Waterer, Grant W. (2003). "The impact of estrogen and progesterone on asthma". Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. 90 (3): 284–91, quiz 291–3, 347. doi:10.1016/S1081-1206(10)61794-2. PMID 12669890.
- ^ Hatfield. "Asthma in Women".
- ^ Marsh, Alex; Gordon, David; Heslop, Pauline; Pantazis, Christina (2000). "Housing Deprivation and Health: A Longitudinal Analysis". Housing Studies. 15 (3): 411. doi:10.1080/02673030050009258. S2CID 154051241.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search