
Back محرك تيار مستمر عديم المسفرات Arabic Безколекторен постояннотоков двигател Bulgarian Bezkartáčový stejnosměrný motor Czech Børsteløs DC-motor Danish Bürstenloser Gleichstrommotor German Motor de imanes permanentes Spanish Harjavaba alalisvoolumootor Estonian موتور بدون جاروبک دیسی Persian Moteur sans balais French Motor de corrente continua sen vasoiriñas Galician

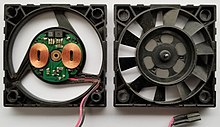
A brushless DC electric motor (BLDC), also known as an electronically commutated motor, is a synchronous motor using a direct current (DC) electric power supply. It uses an electronic controller to switch DC currents to the motor windings producing magnetic fields that effectively rotate in space and which the permanent magnet rotor follows. The controller adjusts the phase and amplitude of the current pulses that control the speed and torque of the motor. It is an improvement on the mechanical commutator (brushes) used in many conventional electric motors.
The construction of a brushless motor system is typically similar to a permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM), but can also be a switched reluctance motor, or an induction (asynchronous) motor. They may also use neodymium magnets[1] and be outrunners (the stator is surrounded by the rotor), inrunners (the rotor is surrounded by the stator), or axial (the rotor and stator are flat and parallel).[2]
The advantages of a brushless motor over brushed motors are high power-to-weight ratio, high speed, nearly instantaneous control of speed (rpm) and torque, high efficiency, and low maintenance. Brushless motors find applications in such places as computer peripherals (disk drives, printers), hand-held power tools, and vehicles ranging from model aircraft to automobiles. In modern washing machines, brushless DC motors have allowed replacement of rubber belts and gearboxes by a direct-drive design.[3]
- ^ Widmer, James D.; Martin, Richard; Kimiabeigi, Mohammed (April 2015), "Electric vehicle traction motors without rare earth magnets", Sustainable Materials and Technologies, 3: 7–13, Bibcode:2015SusMT...3....7W, doi:10.1016/j.susmat.2015.02.001, retrieved 2024-05-20
- ^ Control differences between ac induction motor and brushless dc motor? – Electrical Engineering Stack Exchange. electronics.stackexchange.com (2019-12-20). Retrieved on 2019-12-26.
- ^ "What is a BLDC Motor in a Washing Machine?". Dumb Little Man. Retrieved 11 June 2019.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search