
Back بوفوتينين Arabic بوفوتينين AZB Bufotenin Czech Bufotenin Danish Bufotenin German Bufotenina Spanish Bufotenina Basque بوفوتنین Persian Bufoteniini Finnish Bufoténine French
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | N,N-Dimethyl-5-hydroxytryptamine; 5-Hydroxy-dimethyltryptamine; Bufotenine; Cebilcin |
| Routes of administration | Oral, intravenous |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.971 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
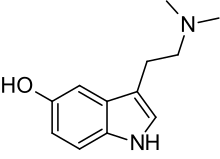
| Formula | C12H16N2O |
| Molar mass | 204.273 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 146 to 147 °C (295 to 297 °F) |
| Boiling point | 320 °C (608 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Bufotenin (5-HO-DMT, bufotenine) is a tryptamine derivative, more specifically, a DMT analog, related to the neurotransmitter serotonin. It is an alkaloid found in some species of mushrooms, plants and toads, especially the skin.
The name bufotenin originates from the toad genus Bufo, which includes several species of psychoactive toads, most notably Incilius alvarius, that secrete bufotoxins from their parotoid glands.[1] Bufotenin is similar in chemical structure to the psychedelics psilocin (4-HO-DMT), 5-MeO-DMT and DMT, chemicals which also occur in some of the same fungus, plant and animal species as bufotenin.
- ^ Bufo Alvarius. AmphibiaWeb. Accessed on May 6, 2007.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search