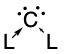
Carbones are a class of molecules containing a carbon atom in the 1D excited state with a formal oxidation state of zero where all four valence electrons exist as unbonded lone pairs.[1] These carbon-based compounds are of the formula CL2 where L is a strongly σ-donating ligand, typically a phosphine (carbodiphosphoranes) or a N-heterocyclic carbene/NHC (carbodicarbenes), that stabilises the central carbon atom through donor-acceptor bonds.[1] Carbones possess high-energy orbitals with both σ- and π-symmetry, making them strong Lewis bases and strong π-backdonor substituents.[2] Carbones possess high proton affinities[3][4] and are strong nucleophiles which allows them to function as ligands in a variety of main group and transition metal complexes.[5] Carbone-coordinated elements also exhibit a variety of different reactivities and catalyse various organic[6][7][8][9] and main group reactions.[10][11]
- ^ a b Frenking, Gernot; Tonner, Ralf (2009). "Divalent carbon(0) compounds". Pure and Applied Chemistry. 81 (4): 597–614. doi:10.1351/PAC-CON-08-11-03. S2CID 98257123.
- ^ Tonner, Ralf; Frenking, Gernot (2008). "Divalent Carbon(0) Chemistry, Part 1: Parent Compounds". Chemistry: A European Journal. 14 (11): 3260–3272. doi:10.1002/chem.200701390. PMID 18318020.
- ^ Tonner, Ralf; Öxler, Florian; Neumüller, Bernhard; Petz, Wolfgang; Frenking, Gernot (2006). "Carbodiphosphoranes: The Chemistry of Divalent Carbon(0)". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 45 (47): 8038–8042. doi:10.1002/anie.200602552. PMID 17075933.
- ^ Tonner, Ralf; Frenking, Gernot (2007). "C(NHC)_2: Divalent Carbon(0) Compounds with N-Heterocyclic Carbene Ligands-Theoretical Evidence for a Class of Molecules with Promising Chemical Properties". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 46 (45): 8695–8698. doi:10.1002/anie.200701632. PMID 17924383.
- ^ Tonner, Ralf; Frenking, Gernot (2008). "Divalent Carbon(0) Chemistry, Part 2: Protonation and Complexes with Main Group and Transition Metal Lewis Acids". Chemistry: A European Journal. 14 (11): 3273–3289. doi:10.1002/chem.200701392. PMID 18318021.
- ^ Pranckevicius, Conor; Fan, Louie; Stephan, Douglas (2015). "Cyclic Bent Allene Hydrido-Carbonyl Complexes of Ruthenium: Highly Active Catalysts for Hydrogenation of Olefins". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 137 (16): 5582–5589. doi:10.1021/jacs.5b02203. PMID 25855868.
- ^ Hsu, Yu-Chen; Chen, Jiun-Shian; Lin, Bo-Chao; Chen, Wen-Ching; Chan, Yi-Tsu; Ching, Wei-Min; Yap, Glenn; Hsu, Chao-Ping; Ong, Tiow-Gan (2014). "Synthesis and Isolation of an Acyclic Tridentate Bis(pyridine)carbodicarbene and Studies on Its Structural Implications and Reactivities". Angewandte Chemie. 127 (8): 2450–2454. doi:10.1002/ange.201406481.
- ^ Goldfogel, Matthew; Roberts, Courtney; Meek, Simon (2014). "Intermolecular Hydroamination of 1,3-Dienes Catalyzed by Bis(phosphine)carbodicarbene-Rhodium Complexes". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 136 (17): 6227–6230. doi:10.1021/ja502275w. PMID 24742315.
- ^ Roberts, Courtney; Matías, Desirée; Goldfogel, Matthew; Meek, Simon (2015). "Lewis acid Activation of Carbodicarbene Catalysts for Rh-Catalyzed Hydroarylation of Dienes". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 137 (20): 6488–6491. doi:10.1021/jacs.5b03510. PMID 25961506.
- ^ Walley, Jacob; Breiner, Grace; Wang, Guocang; Dickie, Diane; Molino, Andrew; Dutton, Jason; Wilson, David; Gilliard Jr., Robert (2019). "s-Block carbodicarbene chemistry: C(sp^3)-H activation and cyclization mediated by a beryllium center". Chemical Communications. 55 (13): 1967–1970. doi:10.1039/C8CC10022E. PMID 30681680. S2CID 59252440.
- ^ Walley, Jacob; Obi, Akachukwu; Breiner, Grace; Wang, Guocang; Dickie, Diane; Molino, Andrew; Dutton, Jason; Wilson, David; Gilliard Jr., Robert (2019). "Cyclic(alkyl)(amino) Carbene-Promoted Ring Expansion of a Carbodicarbene Beryllacycle". Inorganic Chemistry. 58 (16): 11118–11126. doi:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.9b01643. PMID 31380626. S2CID 199437238.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search
