
Back زرنيخات النحاس الثنائي Arabic آرسنات پاخیر (II) AZB Arsenat de coure(II) Catalan Kupfer(II)-arsenat German آرسنات مس (II) Persian Rollandite French Koper(II)arsenaat Dutch Арсенат меди(II) Russian Bakar(II) arsenat Serbo-Croatian Bakar(II) arsenat Serbian
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Copper(II) arsenate
| |
| Other names
Copper arsenate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
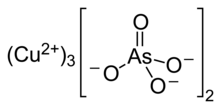
| Cu3(AsO4)2 | |
| Molar mass | 468.48 g/mol |
| Appearance | blue or bluish green powder |
| Density | 5.2 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 1,100 °C (2,010 °F; 1,370 K) |
| insoluble | |
Solubility product (Ksp)
|
7.95×10−36[1] |
| Solubility | soluble in ammonia, dilute acids |
| Hazards | |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 1 mg/m3 (as Cu)[2] |
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 1 mg/m3 (as Cu)[2] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
TWA 100 mg/m3 (as Cu)[2] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Copper arsenate (Cu3(AsO4)2·4H2O, or Cu5H2(AsO4)4·2H2O), also called copper orthoarsenate, tricopper arsenate, cupric arsenate, or tricopper orthoarsenate, is a blue or bluish-green powder insoluble in water and alcohol and soluble in aqueous ammonium and dilute acids. Its CAS number is or .
- ^ John Rumble (June 18, 2018). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (99 ed.). CRC Press. pp. 5–188. ISBN 978-1138561632.
- ^ a b c NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0150". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search