
Back تردد القطع Arabic Freqüència de tall Catalan Grenzfrequenz German Limfrekvenco Esperanto Frecuencia de corte Spanish Lõikesagedus Estonian فرکانس قطع Persian Fréquence de coupure French Frequenza di taglio Italian 遮断周波数 Japanese

In physics and electrical engineering, a cutoff frequency, corner frequency, or break frequency is a boundary in a system's frequency response at which energy flowing through the system begins to be reduced (attenuated or reflected) rather than passing through.
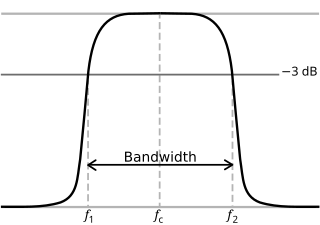
Typically in electronic systems such as filters and communication channels, cutoff frequency applies to an edge in a lowpass, highpass, bandpass, or band-stop characteristic – a frequency characterizing a boundary between a passband and a stopband. It is sometimes taken to be the point in the filter response where a transition band and passband meet, for example, as defined by a half-power point (a frequency for which the output of the circuit is approximately −3.01 dB of the nominal passband value). Alternatively, a stopband corner frequency may be specified as a point where a transition band and a stopband meet: a frequency for which the attenuation is larger than the required stopband attenuation, which for example may be 30 dB or 100 dB.
In the case of a waveguide or an antenna, the cutoff frequencies correspond to the lower and upper cutoff wavelengths.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search
