Back Delta Capricorni Afrikaans ذنب الجدي Arabic Deneb Algedi AST Delta Capricorni BS Delta de Capricorn Catalan HD207098 CE Deneb Algiedi Czech Deneb Algedi German Ντενέμπ Αλτζέντι Greek Deneb Algedi Spanish
| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Capricornus |
| Right ascension | 21h 47m 02.44424s[1] |
| Declination | −16° 07′ 38.2335″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 2.81[2] (2.81 (- 2.90) - 3.05)[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | A7m III[2] (kA5hF0mF2III)[4] |
| U−B color index | +0.07[5] |
| B−V color index | +0.31[5] |
| Variable type | Eclipsing binary (Algol-type)[3] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −6.3[6] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: +261.70[1] mas/yr Dec.: −296.70[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 84.27 ± 0.19 mas[1] |
| Distance | 38.70 ± 0.09 ly (11.87 ± 0.03 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | +2.48[7] |
| Orbit[8] | |
| Primary | δ Cap Aa |
| Companion | δ Cap Ab |
| Period (P) | 1.0227683 days |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0 (assumed) |
| Inclination (i) | 72.5° |
| Periastron epoch (T) | 2,448,105.793 ± 0.003 HJD |
| Semi-amplitude (K1) (primary) | 75.3 ± 1.0 km/s |
| Details | |
| δ Cap Aa | |
| Mass | 2.0[8] M☉ |
| Radius | 1.91[8] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 8.5[7] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 3.66[9] cgs |
| Temperature | 7,301[9] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | –0.13[9] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 105[10] km/s |
| δ Cap Ab | |
| Mass | 0.73[8] M☉ |
| Radius | 0.9[8] R☉ |
| Temperature | 4,500[8] K |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
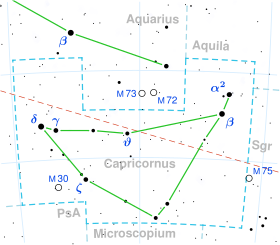
Delta Capricorni, or δ Capricorni, is a binary star located 38.7 light-years from the Sun in the constellation of Capricornus (the Sea Goat). The system consists of an eclipsing binary,[12] Delta Capricorni A, and two visual companions that are over 10 magnitudes fainter, labeled B and C.[13] Delta Capricorni A's two components are designated Delta Capricorni Aa (formally named Deneb Algedi /ˌdɛnɛb ælˈdʒiːdiː/, the traditional name of the system)[14][15] and Ab. The primary star, Aa, is a white giant and the combined light of Aa and Ab makes it the brightest star in the constellation.
Delta Capricorni is 2.6 degrees south of the ecliptic and can be occulted by the Moon, and (rarely) by planets.[16]
- ^ a b c d e Cite error: The named reference
aaa474_2_653was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
aaa446_2_785was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
gcvswas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
aj126_4_2048was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
aj79_1290was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
gcsrvwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Anderson2012was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e f Cite error: The named reference
jrasc86_2_99was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c Cite error: The named reference
apj658_2_1264was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
aaa393_897was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
SIMBADwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
mnras389_2_869was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Washington Double Star Catalog". United States Naval Observatory. Archived from the original on 14 February 2011. Retrieved 2 January 2018.
- ^ Kunitzsch, Paul; Smart, Tim (2006). A Dictionary of Modern star Names: A Short Guide to 254 Star Names and Their Derivations (2nd rev. ed.). Cambridge, Massachusetts: Sky Pub. ISBN 978-1-931559-44-7.
- ^ "Naming Stars". IAU.org. Retrieved 16 December 2017.
- ^ Herr, Richard B. (April 1969). "Identification List of Spectroscopic and Eclipsing Binaries Subject to Occultations by the Moon". Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific. 81 (479): 105. Bibcode:1969PASP...81..105H. doi:10.1086/128748. S2CID 123513287.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search