
Back افعى الجرسية الشرقيه ARZ Източна диамантена гърмяща змия Bulgarian Cròtal adamantí Catalan Crotalus adamanteus CEB Chřestýš diamantový Czech Diamant-Klapperschlange German Κροταλίας ο αδαμάντινος Greek Crotalus adamanteus Spanish Crotalus adamanteus Basque مار زنگی پشتالماسی شرقی Persian
| Eastern diamondback rattlesnake | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Suborder: | Serpentes |
| Family: | Viperidae |
| Genus: | Crotalus |
| Species: | C. adamanteus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Crotalus adamanteus Palisot de Beauvois, 1799
| |
| |
| Synonyms[3] | |
| |
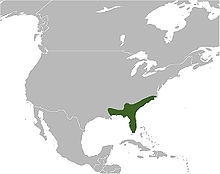
The eastern diamondback rattlesnake (Crotalus adamanteus)[4][5] is a species of pit viper in the family Viperidae. The species is endemic to the Southeastern United States. It is one of the heaviest venomous snakes in the Americas and the largest rattlesnake. No subspecies are recognized.[6]
- ^ Hammerson, G.A. (2007). "Crotalus adamanteus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2007: e.T64308A12762249. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2007.RLTS.T64308A12762249.en. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
- ^ "Crotalus adamanteus". NatureServe Explorer. Retrieved 17 April 2024.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
McD99was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Klauber LM (1997) [First published 1956]. Rattlesnakes: Their Habitats, Life Histories, and Influence on Mankind (Second ed.). Berkeley, CA: University of California Press. ISBN 0-520-21056-5.
- ^ Fichter GS (1982). Poisonous Snakes: A First Book. Franklin Watts. ISBN 0-531-04349-5.
- ^ "Crotalus adamanteus ". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved 28 November 2006.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search

