
Back النظام المجازي للمعرفة الإنسانية Arabic Diderot’n ja d’Alembertin puu Finnish Système figuré des connaissances humaines French 具象人类知识系统 Chinese
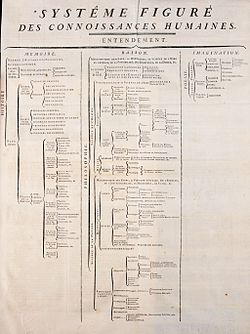
The "figurative system of human knowledge" (French: Système figuré des connaissances humaines), sometimes known as the tree of Diderot and d'Alembert, was a tree developed to represent the structure of knowledge itself, produced for the Encyclopédie by Jean le Rond d'Alembert and Denis Diderot.
The tree was a taxonomy of human knowledge, inspired by Francis Bacon's The Advancement of Learning. The three main branches of knowledge in the tree are: "Memory"/History, "Reason"/Philosophy, and "Imagination"/Poetry.
Notable is the fact that theology is ordered under philosophy. The historian Robert Darnton has argued that this categorization of religion as being subject to human reason, and not a source of knowledge in and of itself (revelation), was a significant factor in the controversy surrounding the work.[1] "Knowledge of God" is only a few nodes away from divination and black magic.
- ^ Robert Darnton, "Philosophers Trim the Tree of Knowledge: The Epistemological Strategy of the Encyclopedie," The Great Cat Massacre and Other Episodes in French Cultural History (New York: Basic Books, Inc., 1984), 191-213.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search