
Back تاريخ بنغلاديش Arabic Historia de Bangladex AST Banqladeş tarixi Azerbaijani Бангладеш тарихы Bashkir Гісторыя Бангладэш Byelorussian История на Бангладеш Bulgarian বাংলাদেশের ইতিহাস Bengali/Bangla বাংলাদেশর ইতিহাস BPY Història de Bangladesh Catalan Geschichte Bangladeschs German
This article may be too long to read and navigate comfortably. (August 2024) |
| History of Bangladesh |
|---|
 |
|
|
| Part of a series on the |
| Culture of Bangladesh |
|---|
 |
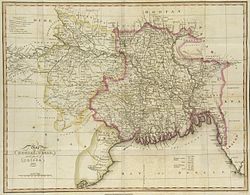
The history of Bangladesh dates back over four millennia to the Chalcolithic period. The region's early history was characterized by a succession of Hindu and Buddhist kingdoms and empires that fought for control over the Bengal region. Islam arrived in the 8th century and gradually became dominant from the early 13th century with the conquests led by Bakhtiyar Khalji and the activities of Sunni missionaries like Shah Jalal. Muslim rulers promoted the spread of Islam by building mosques across the region. From the 14th century onward, Bengal was ruled by the Bengal Sultanate, founded by Fakhruddin Mubarak Shah, who established an individual currency. The Bengal Sultanate expanded under rulers like Shamsuddin Ilyas Shah, leading to economic prosperity and military dominance, with Bengal being referred to by Europeans as the richest country to trade with. The region later became a part of the Mughal Empire, and according to historian C. A. Bayly, it was probably the empire's wealthiest province.
Following the decline of the Mughal Empire in the early 1700s, Bengal became a semi-independent state under the Nawabs of Bengal, ultimately led by Siraj ud-Daulah. It was later conquered by the British East India Company after the Battle of Plassey in 1757. Bengal played a crucial role in the Industrial Revolution in Britain, but also faced significant deindustrialization. The Bengal Presidency was established during British rule.
The borders of modern Bangladesh were established with the partition of Bengal between India and Pakistan during the Partition of India in August 1947, when the region became East Pakistan as part of the newly formed State of Pakistan following the end of the British rule in the region. The Proclamation of Bangladeshi Independence in March 1971 led to the nine-month-long Bangladesh Liberation War, which culminated in the emergence of the People's Republic of Bangladesh. Independence was declared in 1971.
Since gaining independence, Bangladesh has faced political instability, economic reconstruction, and social transformation. The country experienced military coups and authoritarian rule, notably under General Ziaur Rahman and General Hussain Muhammad Ershad. The restoration of parliamentary democracy in the 1990s saw power alternate between the Awami League, and the Bangladesh Nationalist Party. In recent decades, Bangladesh has achieved significant economic growth, emerging as one of the world's fastest-growing economies, driven by its garment industry, remittances, and infrastructure development. However, it continues to grapple with political instability, human rights issues, and the impact of climate change. The return of the Awami League to power in 2009 under Sheikh Hasina's leadership saw economic progress but criticisms of authoritarianism. Bangladesh has played a critical role in addressing regional issues, including the Rohingya refugee crisis, which has strained its resources and highlighted its humanitarian commitments. The Anti-discrimination Students Movement (Bengali: বৈষম্যবিরোধী ছাত্র আন্দোলন) in July 2024, which tragically claimed numerous young lives, led to the conclusion of the Awami League's 16-year dictatorship, compelling the then Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina to resign on August 5, 2024. Sheikh Hasina is infamously regarded as one of the most oppressive leaders in the nation's history. The period marked a second independence for Bangladesh, as democracy was reinstated through the establishment of an interim government.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search