
Back شريان سباتي باطن Arabic Daxili yuxu arteriyası Azerbaijani Arteria carotis interna German Έσω καρωτίδα Greek Arteria carótida interna Spanish Ezkerreko karotida arteria Basque شریان کاروتید داخلی Persian Artère carotide interne French Arteria carótide interna Galician Nutarnja arterija glave Croatian
| Internal carotid artery | |
|---|---|
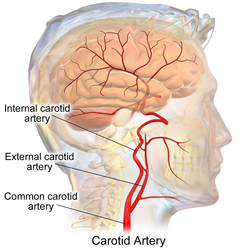 | |
 Arteries of the neck. The internal carotid arteries arise from the common carotid arteries - labeled Common caroti on the figure. | |
| Details | |
| Precursor | 3. Aortic arch |
| Source | Common carotid artery |
| Branches | Ophthalmic, anterior choroidal, anterior cerebral, middle cerebral and posterior communicating artery |
| Vein | Internal jugular vein |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria carotis interna |
| MeSH | D002343 |
| TA98 | A12.2.06.001 |
| TA2 | 4463 |
| FMA | 3947 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The internal carotid artery (Latin: arteria carotis interna) is an artery in the neck which supplies the anterior circulation of the brain.[1]
In human anatomy, the internal and external carotids arise from the common carotid arteries, where these bifurcate at cervical vertebrae C3 or C4. The internal carotid artery supplies the brain, including the eyes,[2] while the external carotid nourishes other portions of the head, such as the face, scalp, skull, and meninges.
- ^ "Carotid artery". WebMD. Retrieved 28 July 2015.
- ^ Kiel JW (2010). "The Ocular Circulation". Integrated Systems Physiology: From Molecule to Function to Disease. 3: 1–81. doi:10.4199/C00024ED1V01Y201012ISP012. PMID 21452447.
The arterial input to the eye is provided by several branches from the ophthalmic artery, which is derived from the internal carotid artery in most mammals.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search