
Back جهد لينارد-جونز Arabic Potencial de Lennard-Jones Catalan Lennard-Jones-potentialet Danish Lennard-Jones-Potential German Potencial de Lennard-Jones Spanish Lennard-Jonesi potentsiaal Estonian پتانسیل لنارد-جونز Persian Lennard-Jonesin potentiaali Finnish Potentiel de Lennard-Jones French פוטנציאל לנארד-ג'ונס HE
| Computational physics |
|---|
 |
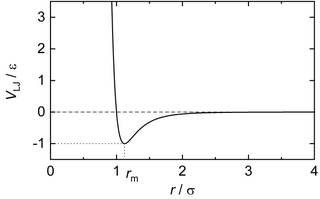
In computational chemistry, molecular physics, and physical chemistry, the Lennard-Jones potential (also termed the LJ potential or 12-6 potential; named for John Lennard-Jones) is an intermolecular pair potential. Out of all the intermolecular potentials, the Lennard-Jones potential is probably the one that has been the most extensively studied.[1][2] It is considered an archetype model for simple yet realistic intermolecular interactions. The Lennard-Jones potential is often used as a building block in molecular models (a.k.a. force fields) for more complex substances.[3] Many studies of the idealized "Lennard-Jones substance" use the potential to understand the physical nature of matter.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
FischerWendlandwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Lenhard, Johannes; Stephan, Simon; Hasse, Hans (2024-05-16). "On the History of the Lennard‐Jones Potential". Annalen der Physik. doi:10.1002/andp.202400115. ISSN 0003-3804.
- ^ Schwerdtfeger, Peter; Wales, David J. (2024-04-26). "100 Years of the Lennard-Jones Potential". Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation. doi:10.1021/acs.jctc.4c00135. ISSN 1549-9618.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search
