
Back نيموديبين Arabic نیمودیپین AZB Nimodipin Welsh Nimodipin German Nimodipina Spanish Nimodipino Basque نیمودیپین Persian Nimodipine French Nimodipina Italian നിമോഡിപ്പിൻ Malayalam
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Nimotop, Nymalize, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a689010 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intravenous, by mouth |
| Drug class | Dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 13% (by mouth) |
| Protein binding | 95% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 8–9 hours |
| Excretion | Feces and Urine |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.060.096 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
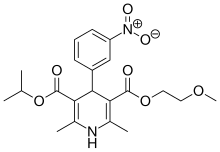
| Formula | C21H26N2O7 |
| Molar mass | 418.446 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 125 °C (257 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Nimodipine, sold under the brand name Nimotop among others, is a calcium channel blocker used in preventing vasospasm secondary to subarachnoid hemorrhage (a form of cerebral hemorrhage). It was originally developed within the calcium channel blocker class as it was used for the treatment of high blood pressure, but is not used for this indication.
It was patented in 1971[3] and approved for medical use in the US in 1988.[4] It was approved for medical use in Germany in 1985.[5]
- ^ "Nimodipine Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. March 15, 2019. Retrieved April 11, 2020.
- ^ "FDA-sourced list of all drugs with black box warnings (Use Download Full Results and View Query links.)". nctr-crs.fda.gov. FDA. Retrieved October 22, 2023.
- ^ GB 1358951, Meyer H, Bossert F, Vater W, Stoepel KN, "New esters, their production, and their medicinal use", published 1974-07-03, assigned to Bayer AG
- ^ "US FDA NDA 018869" (New drug approval from the US FDA). Drugs@FDA.gov Approved Drugs. Food and Drug Administration of the United States (FDA). December 28, 1988. Retrieved April 11, 2019.
Nimodipine (...) approved for the treatment of high blood pressure (...)
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 464. ISBN 9783527607495.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search