
Back Parlement van Botswana Afrikaans برلمان بوتسوانا Arabic Парламент Батсваны Byelorussian Parlamento de Botsuana Spanish Parlement van Botswana Dutch Парламент Ботсваны Russian Palamente ya Botswana Setswana Парламент Ботсвани Ukrainian 博茨瓦纳议会 Chinese
Parliament of Botswana Palamente ya Botswana | |
|---|---|
| 12th Parliament | |
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| Houses | National Assembly |
| History | |
| Founded | 1 March 1965 |
| Leadership | |
Mokgweetsi Masisi since 1 April 2018 | |
Phandu Skelemani since 5 November 2019 | |
Leader of the House | |
Leader of Opposition | |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 65 |
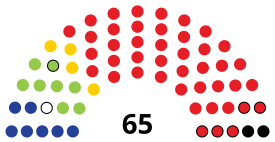 | |
National Assembly political groups | Government (45)
Other opposition (12)
|
| Elections | |
| First-past-the-post voting | |
Last National Assembly election | 23 October 2019 |
Next National Assembly election | By October 2024 |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| National Assembly Chamber Gaborone South-East District | |
| Website | |
| www | |
 |
|---|
| Constitution |
The Parliament of Botswana consists of the President and the National Assembly.[7] In contrast to other parliamentary systems, the Parliament elects the President directly (instead of having both a ceremonial President and a Prime Minister who has real authority as head of government) for a set five-year term of office. A president can only serve 2 full terms. The President is both Head of state and of government in Botswana's parliamentary republican system. Parliament of Botswana is the supreme legislative authority.[8] The President of Botswana is Mokgweetsi Masisi, who assumed the Presidency on 1 April 2018. In October 2019, the 2019 general election was held which saw the return of the Botswana Democratic Party to the power with a majority of 19 seats in the 65 seat National Assembly.
There also exists a body known as Ntlo ya Dikgosi, (The House of Chiefs), which is an advisory body that does not form part of the Parliament.[9]
Botswana is one of only two nations on the African continent (with the other being Mauritius) to have achieved a clean record of free and fair elections since independence, having held 11 elections since 1966 without any serious incidents of corruption.[10]
- ^ "Masisi's SEMPs A Tough Assignment". Mmegi. The Monitor. 4 November 2019. Retrieved 22 July 2021.
- ^ "FAQs". parliament.gov.bw. Parliament of Botswana. Retrieved 22 July 2021.
2 are Ex-officios being the President and The Speaker
- ^ Tlhankane, Mompati (1 August 2022). "The determined, unyielding Keorapetse". Mmegi. Retrieved 31 October 2023.
- ^ Tlhankane, Mompati (5 June 2023). "UDC accused of destabilising BCP". Mmegi. Retrieved 6 June 2023.
The BCP is currently stuck in the coalition because it cannot afford to trigger by-elections because of a new piece of legislation that prohibits Parliament floor crossing.
- ^ Selatlhwa, Innocent (22 May 2023). "Dow: Democracy under threat". Mmegi Online. Retrieved 7 April 2024.
- ^ "DOW JOINS BOTSWANA CONGRESS PARTY". DailyNews. 22 May 2023. Retrieved 7 April 2024.
- ^ Constitution of the Republic of Botswana, 1966
- ^ "Parliament of Botswana". Parliament of Botswana. 19 March 2021. Retrieved 19 March 2021.
- ^ Proctor, J. H. (1968). "The House of Chiefs and the Political Development of Botswana". The Journal of Modern African Studies. 6 (1): 59–79. doi:10.1017/S0022278X00016670. ISSN 0022-278X. JSTOR 158677. S2CID 154486897.
- ^ US State Department
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search