| Main Portal page | Indices | Projects |
 |
 |

| |
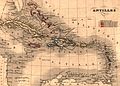
The Caribbean (/ˌkærɪˈbiːən, kəˈrɪbiən/ KARR-ih-BEE-ən, kə-RIB-ee-ən, locally /ˈkærɪbiːæn/ KARR-ih-bee-an; Spanish: el Caribe; French: les Caraïbes; Dutch: de Caraïben) is a subregion of the Americas that includes the Caribbean Sea and its islands, some of which are surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some of which border both the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean; the nearby coastal areas on the mainland are sometimes also included in the region. The region is south-east of the Gulf of Mexico and Northern America, east of Central America, and north of South America.
Situated largely on the Caribbean Plate, the region has more than 700 islands, islets, reefs, and cays. Island arcs delineate the northern and eastern edges of the Caribbean Sea: the Greater Antilles in the north and the Lesser Antilles, which includes the Leeward Antilles, in the east and south. The nearby Lucayan Archipelago, comprising The Bahamas and the Turks and Caicos Islands, is considered to be a part of the Caribbean despite not bordering the Caribbean Sea. All the islands in the Antilles plus the Lucayan Archipelago form the West Indies, which is often interchangeable with the term Caribbean. On the mainland, Belize, the eastern and northern coasts of Central and South American countries such as the Bay Islands Department of Honduras, the North and South Caribbean Autonomous Regions of Nicaragua, the Limón Province of Costa Rica, and the Archipelago of San Andrés, Providencia and Santa Catalina of Colombia are also considered culturally Caribbean. French Guiana, Guyana, Panama, and Suriname are often included as parts of the Caribbean due to their political and cultural ties with the region.
Geopolitically, the islands of the Caribbean are often regarded as a subregion of North America, though sometimes they are included in Middle America or left as a subregion of their own; alternately, the term "Caribbean" may have the intended exclusion, or even unintentional inclusion, as part of Latin America. Generally the Caribbean area is organized into 33 political entities, including 13 sovereign states, 12 dependencies, historical disputed territories have existed, and seven other overseas territories. From 15 December 1954 to 10 October 2010, there was a territory known as the Netherlands Antilles composed of five islands, all of which were Dutch dependencies. From 3 January 1958 to 31 May 1962, there was also a short-lived political union called the British West Indies Federation composed of ten English-speaking Caribbean territories, all of which were then British dependencies. (Full article...)
Manuel Arístides Ramírez Onelcida (born May 30, 1972) is a Dominican-American former professional baseball outfielder. He played in Major League Baseball (MLB) for parts of 19 seasons. He played with the Cleveland Indians, Boston Red Sox, Los Angeles Dodgers, Chicago White Sox, and Tampa Bay Rays before playing one season at the Chinese Professional Baseball League in Taiwan. Ramirez is recognized for having great batting skill and power. He was a nine-time Silver Slugger and was one of 28 players to hit 500 career home runs. His 21 grand slams are third all-time, and his 29 postseason home runs are the most in MLB history. He appeared in 12 All-Star Games, with a streak of eleven consecutive games beginning in 1998 that included every season that he played with the Red Sox.
Ramirez was born in Santo Domingo, Dominican Republic. When he was 13 years old, he moved to New York City with his parents, Onelcida and Aristides. He attended George Washington High School and became a baseball standout. He was drafted by the Cleveland Indians in the first round of the 1991 MLB draft, 13th overall. He made his MLB debut on September 2, 1993. (Full article...)Selected geography article -

Montserrat (/ˌmɒntsəˈræt/ MONT-sə-RAT) is a British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean. It is part of the Leeward Islands, the northern portion of the Lesser Antilles chain of the West Indies. Montserrat is about 16 km (10 mi) long and 11 km (7 mi) wide, with roughly 40 km (25 mi) of coastline. It is nicknamed "The Emerald Isle of the Caribbean" both for its resemblance to coastal Ireland and for the Irish ancestry of many of its inhabitants. Montserrat is the only non-fully sovereign full member of the Caribbean Community and the Organisation of Eastern Caribbean States.
On 18 July 1995, the previously dormant Soufrière Hills volcano, in the southern part of the island, became active. Eruptions destroyed Montserrat's Georgian era capital city of Plymouth. Between 1995 and 2000, two-thirds of the island's population was forced to flee, primarily to the United Kingdom, leaving fewer than 1,200 people on the island in 1997 (rising to nearly 5,000 by 2016). The volcanic activity continues, mostly affecting the vicinity of Plymouth, including its docking facilities, and the eastern side of the island around the former W. H. Bramble Airport, the remnants of which were buried by flows from volcanic activity on 11 February 2010. (Full article...)Selected fare or cuisine -

Did you know? -

- ...that Fort San Felipe del Morro in Puerto Rico (pictured) was used to stand in for an African slave fortress in the 1996 motion picture "Amistad" by Steven Spielberg?
- ...that Eastern Cuban cuisine forms the basis of criollo cooking, which shares a great deal of recipes with other Caribbean cuisines, but has the distinctive difference of making almost no use of peppers?
- ...that Joséphine de Beauharnais, the first wife of Napoléon Bonaparte and thus the first Empress of the French was born in Les Trois-Îlets, Martinique in 1763?
Related portals
Wikiproject

The palm family, Arecaceae, is widespread in the Caribbean. Globally there are about 191 genera and 2339 species as reported in 2004 by Carlo Morici. Their distribution is biased toward islands – 36% of genera and 52% of species are found only on islands, while 32% of genera and 6% of species are found only on continents. Sixty-two percent of monotypic genera are found only on islands.
Phytogeographically, the Caribbean region is often considered to include the coastal plains of the United States (including south Florida), Mexico (especially the Yucatan), Belize, Colombia and Venezuela. Most species either have a wide distribution which includes part of the Caribbean, or are endemic to the Greater Antilles. Of the islands in the Caribbean, Cuba has the most species of palm, followed by Hispaniola. The Windward and Leeward Islands have the fewest. The palm flora of Trinidad and Tobago consists primarily of species with a South American distribution. Three genera of palm are endemic to the Greater Antilles: Calyptronoma, Hemithrinax and Zombia. Although nearly ubiquitous in the region, the coconut (Cocos nucifera) is not native to the Caribbean. The Caribbean species in the genus Copernicia are all Greater Antillean endemics; two species are restricted to Hispaniola, while the others are restricted to Cuba.
(Full article...)Selected image -

The Barbadoes Mulatto Girl, by Agostino Brunias,
Selected music -
General images
Caribbean topics
Categories
New articles
Rules | Match log | Results page (for watching) | Last updated: 2024-05-31 20:01 (UTC)
Note: The list display can now be customized by each user. See List display personalization for details.
- Starshield (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Mykhal (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-31, score: 16
- Goddess Of The Night (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Haretysh23 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-31, score: 48
- Lucca (surname) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by MrKeefeJohn (talk · contribs · new pages (33)) started on 2024-05-31, score: 16
- Haiti at the 2024 Summer Olympics (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Mypurplelightsaber (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2024-05-31, score: 16
- Florence Cassell (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Deathinparadisefan11 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-05-31, score: 27
- Scoria brick (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Cakelot1 (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2024-05-31, score: 16
- History of Peru (1948–1956) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by AlejandroFC (talk · contribs · new pages (34)) started on 2024-05-31, score: 16
- Héctor Camacho vs. Roberto Durán (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Beast from da East (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-05-31, score: 16
- 2024 Birthday Honours (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Nford24 (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-05-31, score: 24
- Tania Ramos González (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Fadesga (talk · contribs · new pages (24)) started on 2024-05-31, score: 16
- Anisha Gibbons (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Hildreth gazzard (talk · contribs · new pages (197)) started on 2024-05-30, score: 16
- Big Sexy (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 162 etc. (talk · contribs · new pages (21)) started on 2024-05-30, score: 16
- Lynnzee Brown (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Theworldgymnast1 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-05-30, score: 16
- Gujarati diaspora (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Fadesga (talk · contribs · new pages (24)) started on 2024-05-30, score: 16
- List of 7.62×54mmR firearms (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Jauhsekali (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-05-30, score: 16
- Mélanie Renaud (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Cavarrone (talk · contribs · new pages (38)) started on 2024-05-30, score: 16
- SEW (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Oshin2024 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-30, score: 16
- Unaccompanied Refugee Minors Program (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by NuanceQueen (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-05-30, score: 32
- David Hinds (gridiron football) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by WikiOriginal-9 (talk · contribs · new pages (46)) started on 2024-05-30, score: 16
- Hudson Tannis (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Cheney123 (talk · contribs · new pages (25)) started on 2024-05-29, score: 32
- 2024 Caribbean Queen's Tournament (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Yoblyblob (talk · contribs · new pages (31)) started on 2024-05-29, score: 32
- Nahuatlea (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Tom Radulovich (talk · contribs · new pages (64)) started on 2024-05-29, score: 16
- Czech First League records and statistics (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by FromCzech (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2024-05-29, score: 48
- Lismar: Bzrp Music Sessions, Vol. 60 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Gelo DemonPlayer (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-29, score: 16
- Kenneth Elliston Poyser (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by C411978 (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2024-05-29, score: 16
- Caritas Ecuador (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Bdx (talk · contribs · new pages (14)) started on 2024-05-29, score: 16
- Albisu Theatre (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by EssNS (talk · contribs · new pages (34)) started on 2024-05-29, score: 16
- Cienfuegos Yacht Club (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by EssNS (talk · contribs · new pages (34)) started on 2024-05-29, score: 16
- Samana Bay Company of Santo Domingo (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Gloryto11 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-29, score: 16
- Vincent Beache (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Cheney123 (talk · contribs · new pages (25)) started on 2024-05-28, score: 16
- 39th Guadalajara International Film Festival (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by JuliánLeiva66 (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-05-28, score: 16
- Eslinda Núñez (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Fadesga (talk · contribs · new pages (24)) started on 2024-05-28, score: 16
- Moroccan expedition (1843-45) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Dencoolast33 (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-05-24, score: 16
- Toma de Bayamo (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Pavansur (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-05-28, score: 40
- 2000 Guam presidential caucuses (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Memevietnam98 (talk · contribs · new pages (24)) started on 2024-05-28, score: 16
- 2000 Guam Republican presidential caucuses (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Memevietnam98 (talk · contribs · new pages (24)) started on 2024-05-28, score: 16
- 1970 Haitian coup attempt (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by TheBrowniess (talk · contribs · new pages (25)) started on 2024-05-28, score: 32
- Romell Glave (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Hildreth gazzard (talk · contribs · new pages (197)) started on 2024-05-28, score: 16
- Plaza de Armas (Havana) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by EssNS (talk · contribs · new pages (34)) started on 2024-05-28, score: 16
- Stephanie Murphy (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by BilledMammal (talk · contribs · new pages (199)) started on 2024-05-28, score: 16
- Energia (album) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by BilledMammal (talk · contribs · new pages (199)) started on 2024-05-28, score: 16
- The Piazza at Havana (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Lord Cornwallis (talk · contribs · new pages (53)) started on 2024-05-28, score: 24
- Leader of the Opposition (Saint Vincent and the Grenadines) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Cheney123 (talk · contribs · new pages (25)) started on 2024-05-28, score: 16
- Extra Musica (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by DejiJJ (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-05-27, score: 16
- Roberto (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by MrKeefeJohn (talk · contribs · new pages (33)) started on 2024-05-27, score: 16
- Digby Stridiron (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Pangetakongex (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-05-27, score: 32
- Osiris Valdés López (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Fadesga (talk · contribs · new pages (24)) started on 2024-05-27, score: 16
- Miramar Yacht Club (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by EssNS (talk · contribs · new pages (34)) started on 2024-05-27, score: 16
- Kralendijk Lighthouse (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by CareAhLine (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-05-27, score: 48
- List of Scabbard and Blade chapters (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rublamb (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-05-27, score: 16
- Froylan (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Toweli (talk · contribs · new pages (112)) started on 2024-05-27, score: 16
- Colonial Secretary of the Bahamas (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ashlar (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-05-27, score: 16
- Angelo Castillo (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Flapolguru (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-27, score: 16
- Hoy (Dominican newspaper) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Mayor C (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-05-26, score: 16
- La Concha Beach Club (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by EssNS (talk · contribs · new pages (34)) started on 2024-05-26, score: 16
- USLHT Columbine (1892) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Jordanroderick (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-26, score: 16
- 2024 SVB Eerste Divisie (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Velocitasgroningen1934 (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-05-26, score: 19
- Casino Español de La Habana (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by EssNS (talk · contribs · new pages (34)) started on 2024-05-26, score: 16
- Big Five Club (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by EssNS (talk · contribs · new pages (34)) started on 2024-05-26, score: 16
- Gerson Garabito (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Muboshgu (talk · contribs · new pages (16)) started on 2024-05-26, score: 16
- Caroline Xavier (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Kippelboy (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-05-26, score: 16
- At What a Price (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by OAnick (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-26, score: 16
- Dichondra micrantha (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Abductive (talk · contribs · new pages (33)) started on 2024-05-26, score: 27
- 2000 American Samoa presidential caucuses (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Memevietnam98 (talk · contribs · new pages (24)) started on 2024-05-26, score: 16
- 2000 American Samoa Republican presidential caucuses (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Memevietnam98 (talk · contribs · new pages (24)) started on 2024-05-26, score: 16
- 2000 American Samoa Democratic presidential caucuses (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Memevietnam98 (talk · contribs · new pages (24)) started on 2024-05-26, score: 16
- Christine Kelly (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Wiki g22l (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-05-26, score: 16
- Capture of the Grand Mughal Fleet (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SKAG123 (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-05-25, score: 40
- Celia V. Monrouzeau Martínez (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Ivan Quiles (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-25, score: 16
- Miss Cosmo International 2024 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by KamyyFallon (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-25, score: 32
- Frank Martínez (architect) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by EssNS (talk · contribs · new pages (34)) started on 2024-05-25, score: 16
- El Bravo de Siempre (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Reppopul (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-25, score: 16
- Santa's Magic Crystal (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 2001:14BB:118:633:91A4:7C0E:BB14:7EB4 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-25, score: 16
- NWA World's Heavyweight Championship (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Pppery (talk · contribs · new pages (39)) started on 2024-05-25, score: 16
- Salvador Molly's (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Another Believer (talk · contribs · new pages (111)) started on 2024-05-25, score: 27
- 1950 Haitian coup d'état (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Vrostky (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2024-05-25, score: 16
- Nayoka Clunis (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Hildreth gazzard (talk · contribs · new pages (197)) started on 2024-05-25, score: 16
- Malik James-King (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Hildreth gazzard (talk · contribs · new pages (197)) started on 2024-05-25, score: 24
- Curaçao Volunteer Corps (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SailingthroughHistory (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-05-25, score: 48
- Sandrey Davison (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Hildreth gazzard (talk · contribs · new pages (197)) started on 2024-05-25, score: 24
- Rikkoi Brathwaite (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Hildreth gazzard (talk · contribs · new pages (197)) started on 2024-05-25, score: 16
- Katia Itzel García (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by GoPurpleNGold24 (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-05-25, score: 48
- Luis Vázquez (baseball) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Stonecold415 (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-05-25, score: 16
- Annaberg, U.S. Virgin Islands (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Beland (talk · contribs · new pages (93)) started on 2024-05-25, score: 16
- Bellevue, U.S. Virgin Islands (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Beland (talk · contribs · new pages (93)) started on 2024-05-25, score: 16
- Altona, U.S. Virgin Islands (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Beland (talk · contribs · new pages (93)) started on 2024-05-25, score: 16
- Bonne Esperance, U.S. Virgin Islands (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Beland (talk · contribs · new pages (93)) started on 2024-05-25, score: 16
- Hermitage, U.S. Virgin Islands (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Beland (talk · contribs · new pages (93)) started on 2024-05-25, score: 16
- Concordia, U.S. Virgin Islands (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Beland (talk · contribs · new pages (93)) started on 2024-05-25, score: 16
- Mount Pleasant, U.S. Virgin Islands (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Beland (talk · contribs · new pages (93)) started on 2024-05-25, score: 16
- Enighed, U.S. Virgin Islands (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Beland (talk · contribs · new pages (93)) started on 2024-05-25, score: 16
- Northside, U.S. Virgin Islands (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Beland (talk · contribs · new pages (93)) started on 2024-05-25, score: 16
- List of military equipment used by UMkhonto we Sizwe (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Katangais (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-25, score: 16
- Botswana Beast (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Kingzwest (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2024-05-25, score: 16
- Charles Maynard (Dominican politician) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Cheney123 (talk · contribs · new pages (25)) started on 2024-05-25, score: 32
- Los Llopis (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Altenmann (talk · contribs · new pages (95)) started on 2024-05-25, score: 16
- 1960 Salvadoran coup d'état (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by TheBrowniess (talk · contribs · new pages (25)) started on 2024-05-24, score: 16
- Latin American wars of independence (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by AHI-3000 (talk · contribs · new pages (20)) started on 2024-05-24, score: 16
- 1961 Salvadoran coup d'état (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by TheBrowniess (talk · contribs · new pages (25)) started on 2024-05-24, score: 16
- El Laguito Cigar Factory (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by EssNS (talk · contribs · new pages (34)) started on 2024-05-24, score: 24
- Pakistan women's cricket team in England and Ireland in 2012 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Hey man im josh (talk · contribs · new pages (405)) started on 2024-05-24, score: 16
- He Knows (Camila Cabello song) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 2600:6C50:7EF0:71E0:A9A9:4471:80C2:7BB4 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-24, score: 16
- Jeffrey Baltus (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Das osmnezz (talk · contribs · new pages (55)) started on 2024-05-24, score: 16
- 2021 Punjab Kings season (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Sammi Brie (talk · contribs · new pages (132)) started on 2024-05-24, score: 16
- 2021 Kolkata Knight Riders season (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Sammi Brie (talk · contribs · new pages (132)) started on 2024-05-24, score: 16
- 2019 Kolkata Knight Riders season (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Sammi Brie (talk · contribs · new pages (132)) started on 2024-05-24, score: 24
- List of Kappa Beta Pi chapters (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rublamb (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-05-24, score: 16
- 2024 World Judo Championships – Mixed team (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by UHShe4Life (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-24, score: 16
- Moonlight Benjamin (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by NotGuyFieri (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-24, score: 16
- Lenny Tavárez (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Sebaspikyaq (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-05-24, score: 16
- Eastern Caribbean-Southeast Asia Chamber (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Bulklana (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-23, score: 16
- List of alumni of Hatfield College, Durham (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Leonstojka (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-23, score: 16
- Caribbean batfish (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by CycoMa1 (talk · contribs · new pages (9)) started on 2024-05-19, score: 27
- 2024–25 NCAA Division I men's basketball season (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Robert McClenon (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2024-05-19, score: 24
- 2023 Rolling Stone en Español Awards (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by JuliánLeiva66 (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-05-23, score: 24
- 1998 FIFA World Cup qualification – CONCACAF third round (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Wburrow (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-23, score: 40
- Mary Young Sewell (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Gamaliel (talk · contribs · new pages (37)) started on 2024-05-23, score: 16
- La Conga (nightclub) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by EssNS (talk · contribs · new pages (34)) started on 2024-05-23, score: 16
- July 2024 Sint Maarten general election (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Number 57 (talk · contribs · new pages (21)) started on 2024-05-22, score: 19
- List of eulipotyphlans (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by PresN (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-05-22, score: 24
- Michel Météry (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by GMoulard (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-05-22, score: 16
- 2024 Porsche Sprint Challenge Great Britain (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by RxxingAddict (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-22, score: 16
- Disney Destiny (ship) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by CANthony0125 (talk · contribs · new pages (16)) started on 2024-05-22, score: 16
- Dick Steinborn (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Kingzwest (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2024-05-22, score: 24
- Arubus N.V. (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Sadfun43! (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-22, score: 16
- Naomi Seymour (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Moondragon21 (talk · contribs · new pages (58)) started on 2024-05-21, score: 16
- Caribbean Fragoza (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Bustedtype888 (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2024-05-21, score: 16
- La Ranger (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Sebaspikyaq (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-05-21, score: 16
- Wrecks of Saint-Pierre harbor (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by GMoulard (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-05-21, score: 32
- Statue of Roberto Clemente (New York City) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Omnis Scientia (talk · contribs · new pages (49)) started on 2024-05-21, score: 16
- 21st Lima Film Festival (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Renknight (talk · contribs · new pages (10)) started on 2024-05-21, score: 16
- Ipomoea setosa (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by WelwitschiaTokarev (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-21, score: 16
- Taíno genocide (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Borboteo (talk · contribs · new pages (14)) started on 2024-05-21, score: 48
- 2024 Little League World Series (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Stan394 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-05-20, score: 24
- 2024 Little League World Series qualification (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Stan394 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-05-20, score: 56
- 22nd Lima Film Festival (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Renknight (talk · contribs · new pages (10)) started on 2024-05-20, score: 24
- MICAL (Bahamas Parliament constituency) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Moondragon21 (talk · contribs · new pages (58)) started on 2024-05-20, score: 16
- Halieutichthys caribbaeus (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by CycoMa1 (talk · contribs · new pages (9)) started on 2024-05-19, score: 32
- Toki (song) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by 222 Goshiy (talk · contribs · new pages (0)) started on 2024-05-14, score: 24
- Johnathan Rodríguez (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Muboshgu (talk · contribs · new pages (16)) started on 2024-05-20, score: 16
- Sam T. Taylor (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Jeffrey Beall (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-05-20, score: 16
- Casimiro Antonio Marte Familia (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by IntergalacticOboist (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-05-20, score: 24
- Montserrat Casas (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Alsoriano97 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-20, score: 16
- Tizzy (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Clarityfiend (talk · contribs · new pages (9)) started on 2024-05-20, score: 16
- Che Simmons (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Hildreth gazzard (talk · contribs · new pages (197)) started on 2024-05-20, score: 24
- Wilfred Benítez vs. Roberto Durán (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Beast from da East (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-05-20, score: 16
- George J. Gmelch (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by SL93 (talk · contribs · new pages (45)) started on 2024-05-20, score: 16
- Morfina (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by DominicanWikiEdit1996 (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-20, score: 16
- Revelation Pt. 2 – The Fruit of Life (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by L to the K (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-05-20, score: 16
- Moenck & Quintana (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by EssNS (talk · contribs · new pages (34)) started on 2024-05-19, score: 16
- Aymeric Priam (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Hildreth gazzard (talk · contribs · new pages (197)) started on 2024-05-19, score: 24
- Heritage Collection Museum (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by LittleT889 (talk · contribs · new pages (7)) started on 2024-05-19, score: 24
- Ideoblothrus curazavius (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by WhatIsAPoggers (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2024-05-17, score: 27
- Frederick Snare (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by EssNS (talk · contribs · new pages (34)) started on 2024-05-19, score: 16
- Theresa Miskimen (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by TJMSmith (talk · contribs · new pages (13)) started on 2024-05-19, score: 16
- Rashtrakutas (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by BilledMammal (talk · contribs · new pages (199)) started on 2024-05-19, score: 16
- Miguel Ángel Moenck (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by EssNS (talk · contribs · new pages (34)) started on 2024-05-19, score: 16
- World Masters League T20 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Clearfrienda (talk · contribs · new pages (45)) started on 2024-05-19, score: 16
- Príamo Tejeda (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Gianlu2790 (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-05-19, score: 16
- Nicolás Quintana (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by EssNS (talk · contribs · new pages (34)) started on 2024-05-19, score: 32
- Nicolás Quintana Arango (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by EssNS (talk · contribs · new pages (34)) started on 2024-05-19, score: 16
- Tonight (Black Eyed Peas and El Alfa song) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Monika Helgesson (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-19, score: 16
- King Tubby Meets Vivian Jackson (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by GanzKnusper (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-05-19, score: 16
- When Magic Hurts (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Abskiee (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-05-19, score: 16
- Tease Me (album) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Hiddenstranger (talk · contribs · new pages (12)) started on 2024-05-19, score: 16
- Drew Thomas (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Cunard (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-05-19, score: 16
- Club Atenas (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by EssNS (talk · contribs · new pages (34)) started on 2024-05-18, score: 16
- Valentin Medrano Pérez (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by IntergalacticOboist (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-05-18, score: 24
- Havana Yacht Club (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by EssNS (talk · contribs · new pages (34)) started on 2024-05-18, score: 16
- Havana Biltmore Yacht and Country Club (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by EssNS (talk · contribs · new pages (34)) started on 2024-05-18, score: 16
- West Indies women's cricket team in Sri Lanka in 2024 (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Goodknowme (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-05-18, score: 16
- Bain Town and Grants Town (Bahamas Parliament constituency) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Moondragon21 (talk · contribs · new pages (58)) started on 2024-05-18, score: 16
- Wayde Watson (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Moondragon21 (talk · contribs · new pages (58)) started on 2024-05-18, score: 16
- Peter Wayne Lewis (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Spinster300 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-05-18, score: 24
- List of country subdivision flags in North America (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by For the nth time (talk · contribs · new pages (4)) started on 2024-05-18, score: 60
- Patrick Olive (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Anavatar (talk · contribs · new pages (8)) started on 2024-05-18, score: 16
- Lakhni'ah Yanuf (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Yusuf Asar Yathar (talk · contribs · new pages (3)) started on 2024-05-18, score: 16
- Biague Na Ntan (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Noahtaylor5042 (talk · contribs · new pages (2)) started on 2024-05-18, score: 16
- Bill Hook (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Jevansen (talk · contribs · new pages (148)) started on 2024-05-18, score: 16
- Atkinson, Dominica (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Moondragon21 (talk · contribs · new pages (58)) started on 2024-05-17, score: 16
- Vedado Tennis Club (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by EssNS (talk · contribs · new pages (34)) started on 2024-05-17, score: 16
- European Union National Identity Cards (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by エンドくさん (talk · contribs · new pages (5)) started on 2024-05-17, score: 40
- Jonathan Falla (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Il lupa (talk · contribs · new pages (6)) started on 2024-05-17, score: 16
- Diles (song) (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Floppykart (talk · contribs · new pages (33)) started on 2024-05-17, score: 16
- Diorygma antillarum (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Esculenta (talk · contribs · new pages (31)) started on 2024-05-17, score: 35
- José Irisarri (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by EssNS (talk · contribs · new pages (34)) started on 2024-05-17, score: 16
- Guillermo Portela (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by EssNS (talk · contribs · new pages (34)) started on 2024-05-17, score: 16
- Porfirio Franca (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by EssNS (talk · contribs · new pages (34)) started on 2024-05-17, score: 16
- Historic Centre of Cuzco (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by AlejandroFC (talk · contribs · new pages (34)) started on 2024-05-16, score: 16
- Isaac P. Mendes (edit | talk | history | links | watch | logs | tools) by Rhaegar I (talk · contribs · new pages (1)) started on 2024-05-16, score: 16
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
Shortcuts to this page: Portal:West Indies • P:CARIB Purge server cache
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search