Back Portal:Klimawandel German Portail:Changement climatique French Portaal:Opwarming van de Aarde Dutch Cổng thông tin:Biến đổi khí hậu Vietnamese
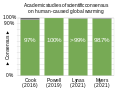
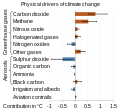
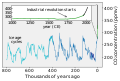
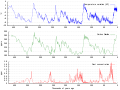
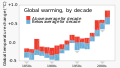
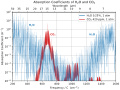
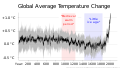
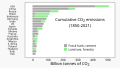
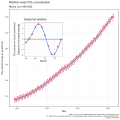
The Climate Change Portal Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth’s climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global temperatures is driven by human activities, especially fossil fuel burning since the Industrial Revolution. Fossil fuel use, deforestation, and some agricultural and industrial practices release greenhouse gases. These gases absorb some of the heat that the Earth radiates after it warms from sunlight, warming the lower atmosphere. Carbon dioxide, the primary gas driving global warming, has increased in concentration by about 50% since the pre-industrial era to levels not seen for millions of years. Climate change has an increasingly large impact on the environment. Deserts are expanding, while heat waves and wildfires are becoming more common. Amplified warming in the Arctic has contributed to thawing permafrost, retreat of glaciers and sea ice decline. Higher temperatures are also causing more intense storms, droughts, and other weather extremes. Rapid environmental change in mountains, coral reefs, and the Arctic is forcing many species to relocate or become extinct. Even if efforts to minimize future warming are successful, some effects will continue for centuries. These include ocean heating, ocean acidification and sea level rise. Climate change threatens people with increased flooding, extreme heat, increased food and water scarcity, more disease, and economic loss. Human migration and conflict can also be a result. The World Health Organization calls climate change one of the biggest threats to global health in the 21st century. Societies and ecosystems will experience more severe risks without action to limit warming. Adapting to climate change through efforts like flood control measures or drought-resistant crops partially reduces climate change risks, although some limits to adaptation have already been reached. Poorer communities are responsible for a small share of global emissions, yet have the least ability to adapt and are most vulnerable to climate change. Many climate change impacts have been observed in the first decades of the 21st century, with 2024 the warmest on record at +1.60 °C (2.88 °F) since regular tracking began in 1850. Additional warming will increase these impacts and can trigger tipping points, such as melting all of the Greenland ice sheet. Under the 2015 Paris Agreement, nations collectively agreed to keep warming "well under 2 °C". However, with pledges made under the Agreement, global warming would still reach about 2.8 °C (5.0 °F) by the end of the century. Limiting warming to 1.5 °C would require halving emissions by 2030 and achieving net-zero emissions by 2050. There is widespread support for climate action worldwide. Fossil fuel use can be phased out by conserving energy and switching to energy sources that do not produce significant carbon pollution. These energy sources include wind, solar, hydro, and nuclear power. Cleanly generated electricity can replace fossil fuels for powering transportation, heating buildings, and running industrial processes. Carbon can also be removed from the atmosphere, for instance by increasing forest cover and farming with methods that capture carbon in soil. (Full article...) Selected article –Climate engineering (also known as geoengineering or climate intervention) is the deliberate large-scale interventions in the Earth’s climate system intended to counteract human-caused climate change. The term commonly encompasses two broad categories: large-scale carbon dioxide removal (CDR) and solar radiation modification (SRM). CDR involves techniques to remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and is generally considered a form of climate change mitigation. SRM aims to reduce global warming by reflecting a small portion of sunlight (solar radiation) away from Earth and back into space. Although historically grouped together, these approaches differ substantially in mechanisms, timelines, and risk profiles, and are now typically discussed separately. Some other large-scale engineering proposals—such as interventions to slow the melting of polar and alpine ice—are also sometimes classified as forms of geoengineering. Some types of climate engineering present political, social and ethical issues. One common objection is that focusing on these technologies could undermine efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Effective governance and international oversight are widely regarded as essential. Major scientific organizations have examined the potential, risks, and governance needs of climate engineering, including the US National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, the Royal Society, the UN Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO), and the World Climate Research Programme. (Full article...) Selected picture – Credit: GRID-Arendal Graph summarizing some of the expected impacts of Global Warming according to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Temperature deviations are from 1990 readings.
WikiProjectsIn the newsAdditional News
Selected biography –Fatih Birol (born 22 March 1958) is a Turkish economist and energy expert, who has served as the executive director of the International Energy Agency (IEA) since 1 September 2015. During his time in charge of the IEA, he has taken a series of steps to modernise the Paris-based international organisation, including strengthening ties with emerging economies like India and China and stepping up work on the clean energy transition and international efforts to reach net zero emissions. Birol was on the Time 100 list of the world's most influential people in 2021, has been named by Forbes magazine among the most influential people on the world's energy scene and recognised by the Financial Times in 2017 as Energy Personality of the Year. Birol is the chairman of the World Economic Forum (Davos) Energy Advisory Board. He is a frequent contributor to print and electronic media and delivers numerous speeches each year at major international summits and conferences. (Full article...) General imagesThe following are images from various climate-related articles on Wikipedia.
Did you know –Related portalsSelected panorama – Credit: USGS Landsat Project: Warming Island – comparison of satellite pictures between 1985 and 2005. Warming Island, Greenland: On January 16th, 2007, the New York Times reported that a new island had been found in Greenland. Warming Island was once thought to be an ice-covered peninsula, but it was exposed as an island when a glacier melted to reveal the strait. This image shows satellite pictures of the island in 1985 when the glacier had firmly tied it to the mainland, in 2002 when there was only a thin bridge of ice, and in 2005 when the bridge of ice has broken to reveal an open water strait. More islands like this may be discovered if the Greenland ice sheet continues to disappear.
Topics
CategoriesWeb resources
Things to do
WikimediaReferences
Discover Wikipedia using portals
|
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search